A Large Intrathoracic Meningocele in a Patient with Neurofibromatosis-1
Article information
Abstract
A large intrathoracic meningocele, a saccular protrusion of the meninges through a dilated intervertebral foramen or a bony defect of the vertebral column, was diagnosed in a 41-year-old female patient showing clinical features of neurofibromatosis-1 (NF-1), including café-au-lait spots, cutaneous neurofibromas, and axillary frecklings and Lisch nodules on the iris. Her daughter and son also had similar manifestations of NF-1. Regular follow-up with periodic imaging was recommended without surgical treatment because there were no signs or symptoms. Meningocele should be differentiated from posterior mediastinal tumors such as neurofibroma, neuroblastoma, and ganglioneuroma because NF-1 has a high risk of tumor formation. We report on this case with a brief review of the literature.
INTRODUCTION
Neurofibromatosis-1 (NF-1), previously referred to as von Recklinghausen's disease, is an autosomal dominant disorder with a birth incidence of 1 in 3,500 [1]. The gene for NF-1 was cloned on chromosome 17q11.2 [2]. Although it manifests with variable signs and symptoms, it mainly affects the skin and peripheral nervous system. NF-1 has a high de novo mutation rate and high risk of tumor formation [3]. Unusual tumors, including carcinoid, pheochromocytoma, brain tumors, and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors occur with higher frequency in NF-1, but other common tumors, such as lung, breast, colon and prostate, are less frequent [4]. Because this disorder involves increased tumor predisposition, the detection of a mass-like lesion raises the possibility of malignancy. In this report, we describe a case of NF-1 presenting with a large intrathoracic mass that was found incidentally.
CASE REPORT
A 41-year-old woman came to the hospital for the evaluation of a lung mass found on a chest radiograph. The patient had no signs or symptoms. However, on physical examination, widespread café-au-lait spots, cutaneous neurofibromas (Fig. 1A), axillary frecklings and reddish brown spots on the iris (Lisch nodules) (Fig. 1B) were present, consistent with the diagnosis of NF-1 [1]. Among the family members, a 14-year-old daughter and 12-year-old son had similar manifestations of NF-1 (Fig. 2). A large mass and a scoliosis were noted on a chest radiograph (Fig. 3). The chest CT and MRI (Fig. 4) showed a 7 cm homogeneous cystic mass with a thin wall in the left paravertebral area, extending into the spinal canal through the T5-6 neural foramen. Clear fluid was withdrawn by needle aspiration and the diagnosis of an intrathoracic meningocele was made. Regular follow-up with periodic imaging was recommended without surgical treatment.

(A) Disseminated café-au-lait spots and cutaneous neurofibromas on the back of the patient. (B) Multiple reddish brown spots (Lisch nodules) on the iris.
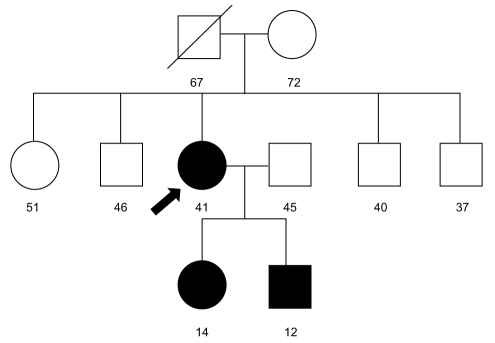
Patient's pedigree. Her father died of gastric cancer at 67 yr old. Her parents, three brothers and sister did not show evidence of neurofibromatosis-1 (NF-1). However, her 14-yr-old daughter and 12-yr-old son showed clinical features of NF-1, such as café-au-lait spots and cutaneous neurofibromas.

(A) A 7 cm low attenuation mass in the left paraspinal space, eroding the left side of T4-T7 vertebrae and extending into the spinal canal through the T5-6 neural foramen on chest CT. (B) An 80 × 58 × 55 mm homogenous, cystic mass in the left paraspinal space and the neural foramen at the left T5-6 level on chest MRI.
DISCUSSION
A spinal meningocele is a saccular protrusion of the meninges through a dilated intervertebral foramen or a bony defect of the vertebral column. Although somewhat common after a laminectomy, a congenital meningocele is relatively rare and usually associated with generalized mesenchymal dysplasia, such as NF-1 or Marfan syndrome [5]. Andrade et al. [6] found that 69% of intrathoracic meningoceles were associated with NF-1 since the first case was reported by Phol in 1933. In the thorax, lateral meningoceles are more frequent because the paravertebral muscles are relatively weak and the pressure gradient between cerebrospinal fluid and thorax is higher. Meningoceles should be differentiated from tumors, especially those that commonly arise from the posterior mediastinum, such as neurofibroma, neuroblastoma, and ganglioneuroma.
Most patients are asymptomatic, but several clinical manifestations can develop depending on size and location of meningoceles. It can cause paraparesis or pain by involvement of the spinal cord, or may compress the lung and mediastinal structures, causing cough, dyspnea, and palpitations [5]. A possible complication is spontaneous rupture with a hydrothorax or hemothorax [7,8].
Surgical treatment is indicated only when the size of the meningocele rapidly increases or when patients are symptomatic due to the compression of surrounding structures by the meningocele [9]. Although laminectomy and intradural repair of the cyst is sufficient for small lesions, a transthoracic approach is required for larger ones to reduce complications such as cord damage and meningopleural fistula.
In conclusion, intrathoracic meningocele is a rare and benign pathology, although surgical treatment is sometimes needed for symptomatic, growing lesions. Meningoceles should be considered in NF-1 patients presenting with a mass-like lesion on a chest radiograph.
Notes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
