A functioning adrenal adenoma and pheochromocytoma in the same adrenal gland: two discrete adrenal incidentalomas
Article information
To the Editor,
An adrenal "incidentaloma" is an adrenal mass, ≥ 1 cm diameter, that is discovered by chance during a radiological examination performed for medical conditions other than adrenal disease [1]. Clinically, about 80% of adrenal incidentalomas are nonfunctional, benign adrenocortical adenomas, 9% cause subclinical Cushing's syndrome, 4% are pheochromocytomas, and only 1% are aldosteronomas. The simultaneous occurrence of a functional adrenocortical adenoma and pheochromocytoma in the same gland is rare [2,3]. A few patients present with symptoms or biochemical laboratory findings compatible with pheochromocytoma and had both a pheochromocytoma and nonfunctioning adrenal cortical adenoma or subclinical Cushing syndrome [2].
Here, we report an extremely rare case of multiple adrenal incidentalomas comprising a functioning adrenal cortical adenoma with resulting adrenal Cushing syndrome and a pheochromocytoma, which was not detected by laboratory findings.
A 58-year-old female with hypertension was hospitalized for evaluation and treatment of acute pneumonia. She complained of respiratory symptoms, edema, easy bruising, central obesity, weight gain, and proximal muscle weakness. Her blood examination showed hypokalemia with K of 2.9 mmol/L. She was taking furosemide, spironolactone, telmisartan, and amlodipine to correct the hypokalemia and control the edematous body changes. Chest computed tomography (CT) taken to evaluate the pneumonia incidentally revealed two discrete masses in the right adrenal gland.
After 2 to 3 weeks of conservative treatment of the pneumonia, the patient was referred to our hospital for evaluation of the adrenal incidentalomas. On physical examination, she had a moon face and central obesity without abdominal cutaneous striae. Her family and social histories were unremarkable. Blood and urine samples were taken to evaluate the functional status of the tumor. She continued to take her antihypertensive medication and diuretics during the tests. The results revealed a normal serum aldosterone, metanephrine, normetanephrine, and 24-hour urinary catecholamines and metanephrines. Cushing syndrome studies showed abnormal values with an elevated serum cortisol (27.7 µg/dL) and 24-hour urinary cortisol (319 µg/day) (Table 1).
An overnight dexamethasone suppression test was conducted to assess cortical secretion to screen for endogenous Cushing syndrome. The resulting cortisol level (22.6 µg/dL) was not suppressed by the overnight dexamethasone test. A standard 2-day dexamethasone suppression test with 0.5 mg per oral every 6 hours for 2 days was conducted for a definitive diagnosis of the Cushing syndrome. The serum cortisol and 24-hour urine cortisol were not suppressed by dexamethasone, remaining greater than 50 nmol/L, which confirmed the diagnosis of Cushing syndrome.
CT of the adrenal glands showed two enhancing nodular lesions in the right adrenal gland that demonstrated rapid washout of contrast media consistent with cortical adenomas (Fig. 1). The patient underwent a laparoscopic right adrenalectomy, and two tumors were identified in the resected gland, as suggested by the CT imaging. The gross findings of the surgical specimens were compatible with adrenal cortical adenomas. The cut section shows two well-defined masses. The larger one, measuring 2.7 × 2.5 × 1.9 cm, was yellow and brown-tan with hemorrhage (Fig. 2A). The other, measuring 0.7 × 0.7 cm, was rubbery and yellow-white (Fig. 2B).
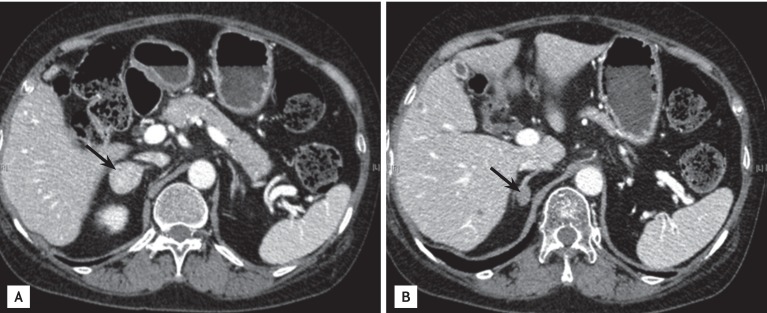
Adrenal computed tomography findings. (A) The mass located at the lateral rim of the adrenal gland was 2.8 cm and its attenuation value was 27.7 Hounsfield unit (HU) initially, 158.5 HU at 1 minute, and 69.8 HU at 15 minutes. (B) The other mass measured 1.4 cm and was located at the medial rim of the adrenal gland. Its attenuation value was 42.67 HU initially, 87 HU at 1 minute, and 57.2 HU at 15 minutes (arrows).

Fresh right adrenalectomy surgical specimen, measuring 6.5 × 4.3 × 2.3 cm and weighing 22 g. The cut section shows two well-defined masses. Pathologically, the larger mass was diagnosed as an adrenal cortical adenoma and the smaller as a pheochromocytoma. (A) The larger mass measures 2.7 × 2.5 × 1.9 cm and is yellow and brown with hemorrhage (arrows). (B) The other mass is 0.7 × 0.7 cm, rubbery, and yellow-white (arrow). (C) Microscopic pathology findings of the right adrenal gland showed a typical adrenal cortical adenoma. The cells are larger, have different cytoplasm, and increased variation in nuclear size compared to a normal adrenal gland (H&E, ×40). (D) The cells have finely granular basophilic cytoplasm, intracytoplasmic hyaline globules, and round and oval nuclei with a prominent nucleolus and variable inclusion-like structures compatible with pheochromocytoma (H&E, ×40). (E) The immunohistochemical staining was positive for chromogranin A (×200).
The patient was stable intraoperatively and postoperatively. She was discharged from the hospital on prednisolone 10 mg per day. After discharge, the pathology report revealed two solid, well-encapsulated tumors with negative resection margins measuring 2.7 × 2.5 × 1.9 cm (Fig. 2A) and 1.0 × 1.0 cm (Fig. 2B). Microscopy and immunohistochemistry confirmed that the larger mass was a cortical adenoma that likely caused the Cushing syndrome (Fig. 2C), while the smaller mass was a pheochromocytoma (Fig. 2D). The immunohistochemical staining for chromogranin A was positive (×200) (Fig. 2E). The postoperative 24-hour urine cortisol was within the normal range (17 µg/day).
A mixed corticomedullary tumor (MCMT) is a rare tumor, defined as a single adrenal lesion composed of a mixture of different cell types derived from both pheochromocytes and cortical cells, which do not share a common embryological origin [4]. Since MCMT was first described in 1969, at least 16 cases have been reported in the English- and French-language literature and more than 30 cases have been reported in three Japanese and two Chinese case series [4]. Coincident adrenal cortical adenomas and pheochromocytomas is not considered a category of MCMT and is extremely rare, especially in the same adrenal gland. There have been only 14 reported cases of a coexisting adrenal cortical adenoma and pheochromocytoma [4]. In all of these cases, there were no typical pheochromocytoma symptoms, and the disease was diagnosed by biochemical laboratory results and imaging studies [1].
Our patient presented with typical Cushingoid features and compatible CT imaging suggestive of an adrenal cortical adenoma. The plasma metanephrine and normetanephrine and the 24-hour urine metanephrine, normetanephrine, and catecholamines were normal, and there was no hypertensive crisis during the surgery. The final pathology examination revealed one mass consistent with an adrenocortical adenoma and a second 1-cm mass consistent with pheochromocytoma. Many pheochromocytomas are diagnosed incidentally during routine radiological examinations or rarely by genetic screening tests for multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndrome or von Hippel-Lindau disease [5]. There have been no incidental discoveries of surgically proven pheochromocytoma, except at autopsy [5]. Such unusual cases should lead us to evaluate the pheochromocytoma further, such as for gene mutations and MEN, if the patient is young.
Roughly 10% of adrenal incidentalomas are bilateral or multiple masses. As in this case, multiple masses in the same adrenal gland that secrete different hormones are possible. Although there are no abnormal hormone tests for pheochromocytoma because the adrenal mass is too small to produce metanephrine, the coexistence of a different type of adrenal adenoma must be considered in all cases. We always test all screening hormone evaluations for adrenal incidentalomas.
In conclusion, we reported the first case of two different adrenal masses, initially diagnosed as functioning adrenal adenomas, but eventually confirmed to be one cortisol-secreting adrenal adenoma and one histopathologically proven pheochromocytoma.
Notes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.