Kommerell’s diverticulum: a rare cause of esophageal subepithelial lesion
Article information
A 56-year-old woman visited our hospital for the evaluation of a subepithelial lesion in the upper esophagus that was found during a screening endoscopy. She did not demonstrate any associated symptoms, such as dysphagia or weight loss, and she denied a family history of gastrointestinal cancer or a history of previous surgery. Upper endoscopy revealed a pulsating lesion, covered with esophageal mucosa, on the posterior side of the upper esophagus (Fig. 1A). On endoscopic ultrasonography, a dilated vessel connected to the right-side aortic arch is seen at the site of the lesion (Fig. 1B). Enhanced computed tomography demonstrated compression of the esophagus by the trachea, the right-side aortic arch, and an aneurysmal dilated vessel (Fig. 2A). Computed tomography angiography revealed the aberrant left subclavian artery, connected to the right-side aortic arch, as the origin of the aneurysmal dilated vessel (Fig. 2B). Therefore, the subepithelial lesion in the upper esophagus was diagnosed as Kommerell’s diverticulum, the aberrant left subclavian artery originating from the right-side aortic arch, causing an extraluminal compression.
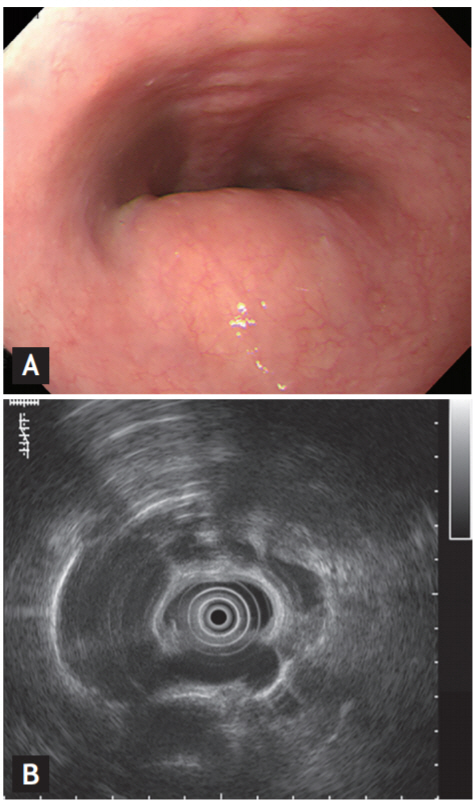
A) Upper endoscopy reveals a pulsating lesion, covered with esophageal mucosa, on the posterior side of the upper esophagus. (B) On endoscopic ultrasonography, a dilated vessel connected to the right-side aortic arch is seen at the site of the lesion.
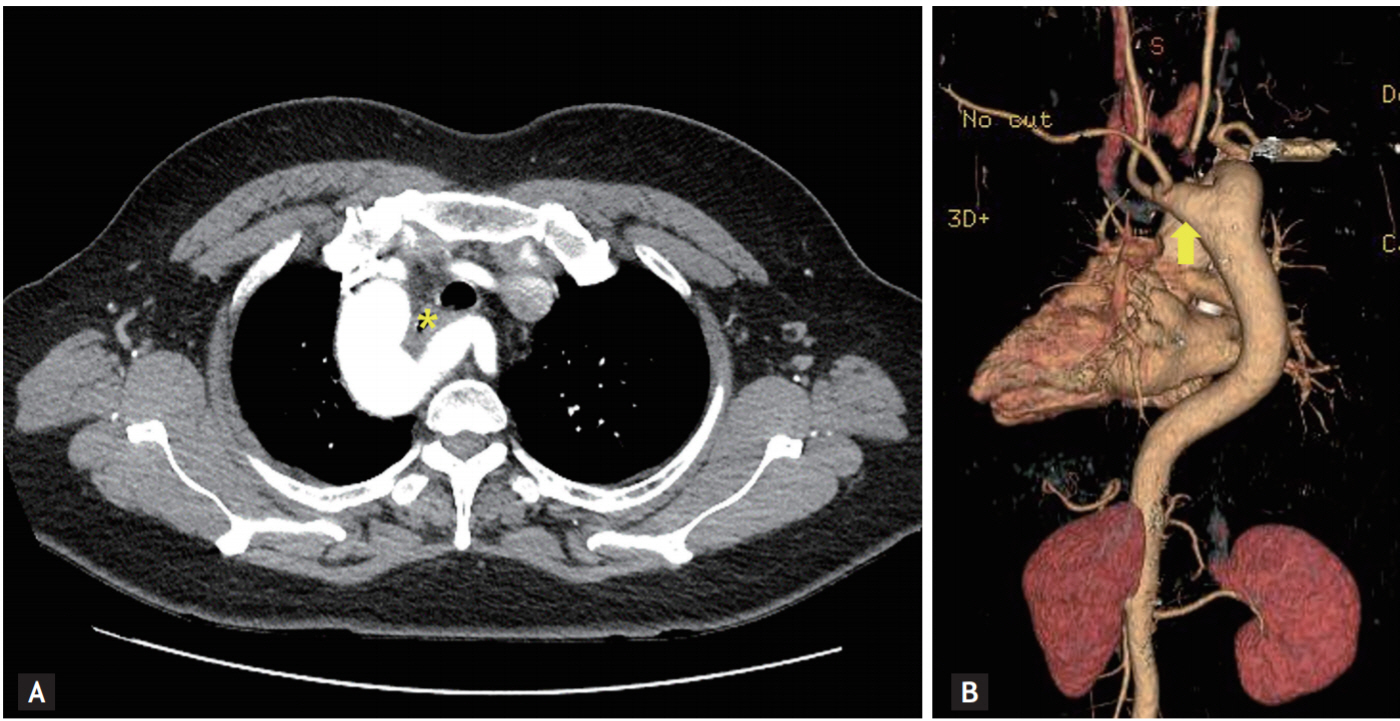
(A) Enhanced computed tomography (CT) demonstrates compression of the esophagus by the trachea, the right-side aortic arch, and an aneurysmal dilated vessel (asterisk). (B) CT angiography reveals the aberrant left subclavian artery, connected to the right-side aortic arch, as the origin of the aneurysmal dilated vessel (arrow).
Kommerell’s diverticulum is a developmental error comprising a remnant of the fourth dorsal aortic arch from which an aberrant subclavian artery originates. Aberrant right subclavian arteries occur in 0.7% to 2.0% of the population, and aberrant left subclavian arteries occur in 0.04% to 0.4%. In about 20% to 60% of individuals with aberrant subclavian arteries, the aberrant vessels are related to Kommerell’s diverticulum. Approximately 5% of adult patients with aberrant subclavian arteries present with symptoms; compression of the esophagus or trachea often leads to dysphasia, dyspnea, cough, recurrent pneumonia, or chest pain. Patients with Kommerell’s diverticulum, presenting with definite symptoms, are indicated for surgical intervention. Treatment for asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic patients with Kommerell’s diverticulum is controversial because of the rareness of the condition. If the aneurysm diameter is > 3 to 5 cm, surgical treatment is usually recommended.
Informed consent was obtained from the patient to publish these images.
Notes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.