|
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 39(2); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
Renal relapse has known to be a poor prognostic factor in patients with lupus nephritis (LN), but there were few studies that identified the risk factors of renal relapse in real world. We conducted this study based on 35-years of experience at a single center to find out predictors of renal relapse in Korean patients with LN after achieving complete response (CR).
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed the clinical, laboratory, pathologic and therapeutic parameters in 296 patients of LN who reached CR. The cumulative risk and the independent risk factors for renal relapse were examined by Kaplan-Meier methods and Cox proportional hazards regression analyses, respectively.
Results
The median follow-up period from CR was 123 months. Renal relapse had occurred in 157 patients. Renal relapse occurred in 38.2%, 57.6% and 67.9% of patients within 5-, 10-, and 20-year, respectively. The age at diagnosis of SLE and LN were significantly younger, and the proportions of severe proteinuria and serum hypoalbuminemia were higher in patients with renal relapse. Interestingly, the proportion of receiving cytotoxic maintenance treatment was higher in patients with renal relapse. In Cox proportional hazards regression analyses, only young-age onset of LN (by 10 years, HR = 0.779, p = 0.007) was identified to independent predictor of renal relapse.
Conclusions
Young-age onset of LN was only independent predictor and the patients with severe proteinuria and serum hypoalbuminemia also tended to relapse more, despite of sufficient maintenance treatment. Studies on more effective maintenance treatment regimens and duration are needed to reduce renal relapse.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by diverse clinical manifestations, ranging from non-life-threatening manifestation such as mucocutaneous symptoms to severe life-threatening organ involvement [1]. Renal involvement is known to be the most commonly affected major organ, with lupus nephritis (LN) occurring in 20–65% of patients with SLE [2]. The presence of LN is associated with poor prognosis including renal function deterioration and mortality [3]. It is known that 10–30% of LN patients progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [4]. Such patients have a 26-fold increase in mortality compared to he general population [5].
To date, many studies have been conducted to find out the predictors of ESRD development and mortality in patients with LN. Among them, renal relapse has been proven to be able to predict poor renal outcomes and mortality [6–11]. Repeated LN flares can exacerbate this poor prognosis [12,13]. Although many attempts have been made to lower the incidence of renal flare and renal flare rate has been shown to be decreased due to long-term maintenance therapy such as mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) [14,15], it is still challenging to prevent renal flare.
Many studies have reported the rate of renal relapse and its predictors. However, only a few recent studies have been conducted in a real-world setting [10,16–18]. According to results of these studies, the renal relapse rate was 30–50% after 10 years of follow-up. Several clinical and pathological factors that could predict renal relapse have been reported. Race and ethnicity could affect the response to treatment and clinical course [19,20], however, those studies only demonstrated the results derived from Whites [17,18] and Hispanics [10] with the exception of our previous study [16]. In addition, the number of study subjects and follow-up periods were relatively small and short.
Previously, we have reported predictive factors for renal relapse based on our experience of Korean patients with LN for 25 years. Since then, MMF has become a major drug for induction and maintenance therapy and new treatment strategies such as calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) have been introduced [21]. Hence, we extended our study to 35 years of experience in a single center. Unlike our previous study on patients who reached partial response (PR) and complete response (CR), we confined patients to those who had achieved CR.
A total of 532 patients with LN who were treated at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital between January 1985 and December 2019 were identified from the chart. All patients met the classification criteria for SLE and LN as defined by 1997 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria [22]. We excluded patients if they were younger than 16 years at diagnosis, those who had other comorbidities such as diabetes that could cause proteinuria, those who were followed up for less than one year after LN diagnosis, those who had poor adherence that could affect treatment response, those who were prescribed any biologic agents, and those who lacked important clinical data. A total of 401 patients were included in our LN cohort. We reviewed their medical charts retrospectively. Among patients in the LN cohort, 296 patients who reached CR were finally enrolled in the present study. This study received approval from the Institutional Review Board of Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital (KC21RASI0046). Written informed consent was waived by the board.
Response to treatment and renal relapse were defined according to 2019 European League Against Rheumatism and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for management of LN [21]. CR was defined as 24-hour urinary protein < 500 mg or urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) < 0.5 and normal or near-normal estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (within 10% of normal eGFR if previously abnormal). As a response criterion, PR and non-responder (NR) were also defined according to the above recommendation. Renal relapse was defined as nephritic flare (reproducible increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 30% or decrease in eGFR by ≥ 10% with active urine sediment and an increase in glomerular hematuria by ≥ 5 red blood cells per high power field irrespective of changes in proteinuria) and proteinuric flare (reproducible doubling of UPCR > 1.0 after CR). The patients were classified as “renal relapse” only if test results consistent with the definition of renal relapse were repeated and the treatment strategy was modified based on the judgement of the expert rheumatologist by integrating other clinical and laboratory findings. eGFR was calculated by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease study equation:
Delayed-onset LN was defined as LN that occurred after the diagnosis of SLE (i.e., it did not occur at the diagnosis of SLE simultaneously). Hypertension (HTN) was defined as a systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg and/or previous diagnosis of HTN and prescription of antihypertensive medication. Acute renal dysfunction was defined as an acute nephritic syndrome (serum creatinine > 1 mg/dL and eGFR ≤ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) or rapidly progressive renal insufficiency [23]. Nephrotic-range proteinuria was defined as 24-hour urinary protein ≥ 3.5 g or a UPUC ≥ 3. Hypoalbuminemia was defined as serum albumin < 3.5 g/dL. Clinically significant hypoalbuminemia was defined as serum albumin < 2.5 g/dL that could cause systemic symptoms such as generalized edema and pleural effusion [24].
Baseline clinical characteristics (including sex, age at the diagnosis of SLE and LN, total follow-up duration from the diagnosis of SLE, LN and CR, medication usage (steroid and hydroxychloroquine [HCQ]) at the diagnosis of LN, body mass index (BMI) and presence of HTN) were collected from medical charts at the diagnosis of LN. Laboratory results including levels of hemoglobin (Hb), platelet (Plt), serum creatinine, eGFR, albumin, uric acid, and the degree of proteinuria at baseline, 6 months and 12 months after treatment initiation were obtained. Immunologic laboratory results including complements level (C3 and C4), anti-nuclear antibody (ANA), anti-dsDNA antibody, anti-Sm/Ro/La/RNP antibodies, and antiphospholipid antibodies (anti-β2 glycoprotein, anti-cardiolipin antibodies, and lupus anticoagulants [LACs]) at baseline were also obtained. In addition, we collected anti-phospholipid Ab positivity as a cumulative manner.
The histological type of LN was reported based on the 1982 modified World Health Organization (WHO) classification or the 2003 International Society of Nephrology/Renal Pathology Society (ISN/RPS) classification criteria according to the date of the biopsy was performed [25,26]. If a case was reported as a mixed type, it was assigned to the dominant class. Activity index (AI) and chronicity index (CI) were calculated using the scoring system of the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) [27]. Detailed pathological findings such as glomerular sclerosis, crescents (cellular/fibro-cellular/fibrous), tubular atrophy, interstitial fibrosis, and intramural thrombi were also recorded. In our hospital, renal biopsies have been reported by two different pathologists simultaneously.
Therapeutic regimens were not standardized since this was a retrospective and observational study. However, all patients received appropriate treatments under the clinical judgement of professional rheumatologists. These therapeutic regimens are acceptable universally. Induction treatment regimens were categorized into steroid only, cyclophosphamide (CYC), MMF, and CNIs. Maintenance treatment regimens were categorized into steroid only, azathioprine (AZP), CYC, MMF, and CNIs. The usage of adjuvant treatment options including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) or angiotensin-receptor blocker (ARB), statin, and HCQ was also obtained. We also investigated delayed time from diagnosis of LN to induction treatment, duration of maintenance, and duration of steroid treatment. We then assessed treatment response at 6 months and 12 months after treatment and determined the time to CR.
All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS statistical software package standard version 25 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Continuous variables are described as mean ± standard deviation and categorical variables are described as counts and percentages. When comparing variables between two groups, Student’s t-test or Mann–Whitney U test was used depending on whether they showed a normal distribution. Chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test was used when comparing categorical variables. Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was performed to identify predictive factors for relapse after achieving CR. Hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval are reported. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to identify time-dependent relapse rate after achieving CR. Log rank test was used to compare two groups. All p values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Among 401 patients of LN treated at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital from 1985 to 2019, 296 patients who reached CR were enrolled. The median follow-up period after the onset of LN and CR were 155 months (range, 82–229 mo) and 123 months (range, 65–203 mo), respectively. Among them, renal relapse occurred in 157 patients during the follow-up period.
Baseline clinical characteristics and laboratory findings of patients at LN onset are presented in Table 1. There were no significant differences in baseline clinical characteristics, including sex, SLE disease duration at the time of LN diagnosis, the proportion of delayed-onset LN, medications used at the time LN development (steroid and HCQ), SLE-DAI, BMI, or the proportion of HTN. Ages at diagnosis of SLE and LN were significantly younger in patients with renal relapse (26.3 vs. 29.7 yr, p = 0.006 and 28.1 vs. 31.7 yr, p = 0.004). Total follow-up duration from LN diagnosis or CR was significant longer in patients with renal relapse, compared with those sustaining CR (172.5 vs. 143.5 mo, p = 0.002 or 150.6 vs. 118.8 mo, p = 0.001).
Regarding laboratory findings, the proportion of low Hb (less than 10 g/dL) and low Plt counts (less than 100,000/μL) were not significantly different between the two groups. Serum Cr, eGFR, and uric acid levels and presence of urinary casts were similar between the two groups. There was no significant difference in the amount of proteinuria or the ratio of nephrotic range proteinuria between the patients who developed renal relapse during the follow-up period and those who had maintained CR state. Serum albumin level, proportion of hypoalbuminemia, and clinically significant hypoalbuminemia were not significantly different either. However, severe proteinuria (over 6 g/day) and severe hypoalbuminemia (less than 2.0 g/dL) were more frequently detected in the group of renal relapse, compared with those sustaining CR state.
As shown in Table 2, most variables including C3 and C4 levels, ANA positivity, anti-dsDNA Ab positivity as well as its titer (by far assay), and the positivity for anti-Sm/Ro/La/RNP Ab were all similar between the two groups. Among anti-phospholipid Ab, LAC was only found more frequently in renal relapse group (15.6 vs. 7.5%, p = 0.041).
Of 296 patients, 228 (77.0%) had undergone a kidney biopsy. Their pathologic findings are presented in Table 3. The proportion of patients who had undergone renal biopsy within 1 month after LN development were similar between the two groups. We did not find any significant differences in pathological findings, including WHO or ISN/RPS classification, AI, and CI. Proportions of those with AI more than 6 and 12 and those with CI more than 4 were also similar between the two groups. There were no significant differences in specific pathological findings such as glomerular sclerosis, cellular/fibro-cellular/fibrous crescents, interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, or intramural thrombi either.
We analyzed types of therapeutic regimens and treatment responses. Results are shown in Table 4. There was no significant difference in time interval from diagnosis of LN to the initiation of induction therapy between the two groups. Treatment for the induction was divided into steroid only, CYC, MMF, and CNIs. The results, as shown in Table 4, did not show any difference between the two groups. Treatment for the maintenance was divided into no maintenance treatment, steroid only, CYC, MMF, AZP, and CNIs. There was a significant difference in maintenance treatment type between the two groups (p = 0.049). We subdivided maintenance treatment type into two groups - cytotoxic maintenance treatment or not. The proportion of those receiving cytotoxic maintenance treatment was significantly higher in the relapsed group (77.4 vs. 62.4%, p = 0.008). Other variables associated with treatment - including duration of maintenance treatment and steroid usage, the proportion of steroid cessation, adjuvant medication like ACEi or ARB, HCQ - showed no significant differences between the two groups. Only statin usage was significantly more frequent in the relapsed group (29.6 vs. 17.0%, p = 0.025).
Treatment responses at 6 months and 12 months after induction were not different between the two groups. In both groups, more than 50% of patients achieved CR after 6 months and more than 60% of patients achieved CR after 12 months. The time to CR was not significantly different between the two groups. Regarding serum eGFR and proteinuria at 6 months and 12 months after starting treatment, only serum eGFR after 6 months was significantly higher in the relapsed group (100.5 vs. 91.7 mL/min/1.73 m2, p = 0.017).
We performed Cox proportional hazards analyses to identify predictors of relapse. Results are summarized in Table 5. We performed univariate analysis with various factors proven to be associated with renal relapse mentioned above. Age at SLE diagnosis (by 10 years, HR 0.781, p = 0.008) and the age at LN diagnosis (by 10 years, HR 0.779, p = 0.007) were associated with relapse. As shown in Table 1, since the period from SLE diagnosis to LN diagnosis did not show a significant difference between the two groups, we selected only one variable, age at LN diagnosis (by 10 years, HR 0.779, p = 0.007), as a predictor of relapse to avoid multicollinearity problem.
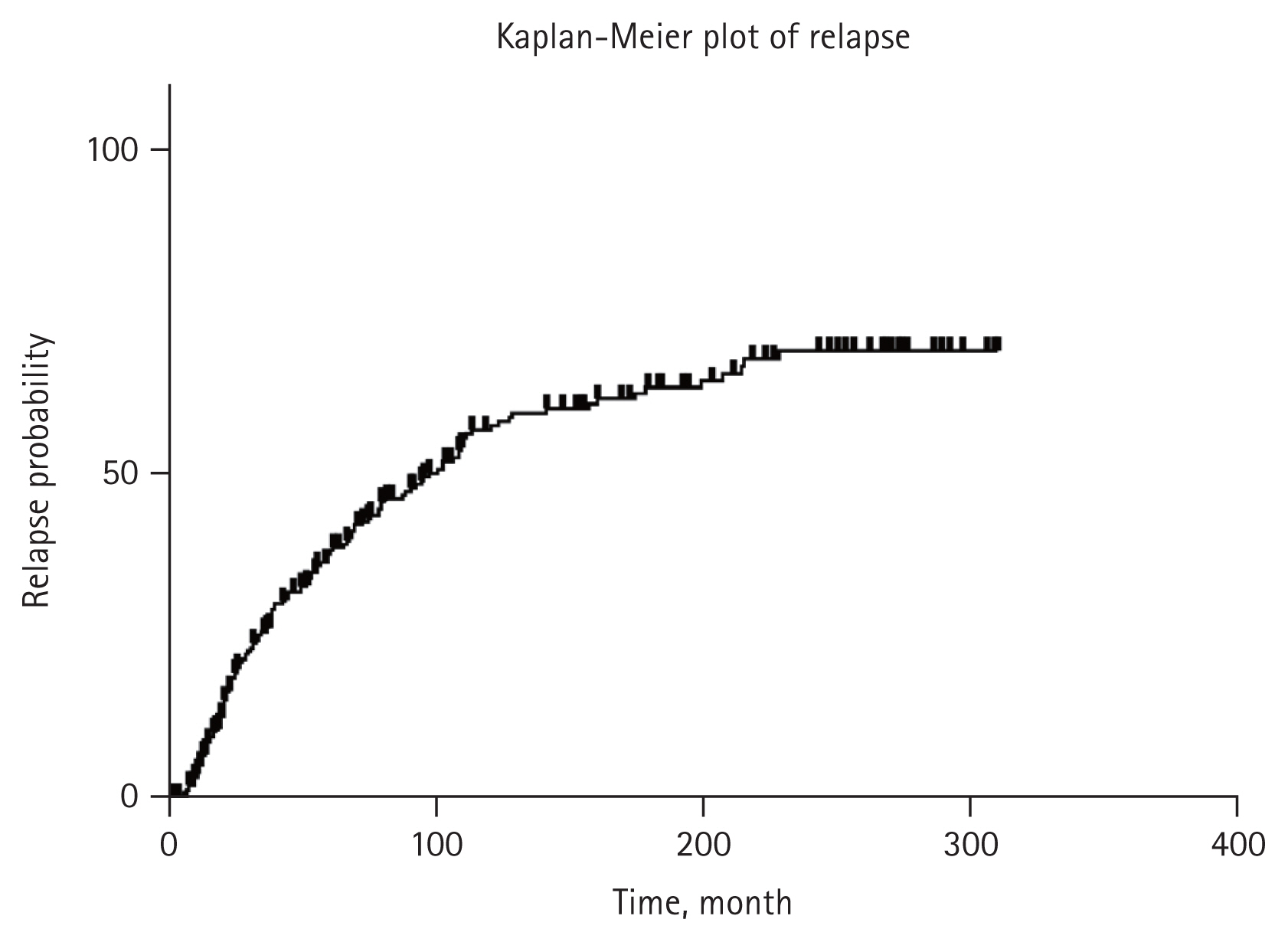
From our study, Kaplan-Meier method showed that renal relapse occurred in 38.2, 57.6, and 67.9% of patients within 5-, 10-, and 20-year after achieving CR, respectively, as shown in Figure 1.
In this study, we evaluated the incidence rate and predictors of renal relapse with 296 patients of LN who achieved CR based on more than 35 years of experience in a single center. We observed renal relapse incidence in 38.2, 57.6, and 67.9% of patients within 5-, 10-, and 20-year after reaching CR, respectively. And we found that young-age onset of LN was the only predictor for renal relapse and the patients with initially severe proteinuria (over 6 g/day) and severe hypoalbuminemia (less than 2.0 g/dL) also tended to relapse more.
It is quite disappointing that so many patients eventually relapsed despite receiving more aggressive cytotoxic maintenance therapy than in the relapse-free group. This is because the patients eventually relapsed despite all of them reaching CR and receiving appropriate doses and durations of following maintenance treatment, although the time to reach CR was different. In patients with LN who developed at young age or initially presented severe proteinuria, currently recommended maintenance treatment may be insufficient in terms of renal protection. And this raises the need for a different strategy - stratified treatment according to the clinical characteristics of the patient.
Previous studies have included both patients achieving CR and PR. Most of these studies showed that failure to reach CR was a risk factor for renal relapse compared with reaching CR [9,10,28–30]. CR itself has been proven to be a protective factor against renal relapse. Thus, we decided to conduct a study only for patients who reached CR. In this study, subjects were followed up for a median of 155 months from the time of LN diagnosis and a median of 123 months from CR. The relapsed group had a significantly longer follow-up duration than the relapse-free group. However, the duration from CR to relapse was 56.4 ± 49.4 months. Most relapses occurred within 120 months. Thus, the follow-up duration 118.8 ± 94.5 months for the relapse-free group was enough to analyze predictors of renal relapse.
There have been reports of relapse rate in the past. However, most of them reported outcomes of controlled studies examining effect of an induction regimen with data mainly from the CYC era [31–34]. Thus, there was a gap with real clinical practice. Recent studies conducted in a real-world setting with whole population of patients with LN (including various pathologic types and treatment regimens) concluded that renal relapse rate was 30–50% after 5 to 10 years of follow-up duration [10,16–18]. Results of our study showed a relapse rate of 38.2% at 5 years and 57.6% at 10 years, which tended to be slightly higher than those of previous studies. This might be because only patients who had reached CR were enrolled in this study. In addition, our hospital is a tertiary and referral hospital. Thus, it might contain more relapsed cases during treatment who are referred from other hospitals.
Among clinical variables reported as predictors of renal relapse so far, age has been reported the most. Previous studies have reported that the younger the age of LN diagnosis or biopsy timing, the higher the probability of renal relapse, including our prior study [7,10,16,32,35–37]. As shown in Table 1, the present study showed the same results with a larger population and a longer follow-up duration. In addition, previous studies have suggested factors that could predict LN relapse from clinical characteristics and laboratory findings at the time of LN diagnosis, including male sex [6,36], delayed-onset LN [38], presence of HTN [6], and elevated baseline creatinine [10]. In the present study, as shown in Table 1, proportions of patients with extremely severe proteinuria (over 6 g) and hypoalbuminemia (less than 2.0 g/dL) were higher in the relapsed group than in the relapse-free group. However, these variables did not appear significant in Cox proportional hazards analysis, suggesting that a different approach might be needed for patients with more severe presentations at the time of initial diagnosis.
In terms of immunological laboratory findings and pathological findings, only LAC positivity was found to be associated with LN relapse, unlike various predictors previously reported. Baseline hypocomplementemia has been reported to be associated with renal relapse [8,39]. However, our results did not show such association. Regarding various autoantibodies, many studies have presented the importance of persistence of anti-dsDNA Ab after 6 months of induction treatment [16,17,37,39]. Our prior study showed the association of anti-Ro Ab negativity with renal relapse [16]. However, our present study with a larger population and a longer follow-up duration did not show such associations (persistence of anti-dsDNA Ab after 6 months of induction treatment between the two groups was 57.8 vs. 55.3%, p = 0.812, not shown in Table 4). The higher incidence of relapse in LAC-positive patients is a previously unreported finding. However, since there was no significant difference in the thromboembolic event occurrence rate between two groups (data are not shown, 29.2 vs. 44.4%, p = 0.438), further research is needed to determine whether there is a clinical relevance. Pathological parameters including diffuse proliferative LN (class IV) itself [35,40], higher AI or CI [7,28,34], and tubulointerstitial lesion in membranous LN (class V) [41] have been proven to be risk factors for renal relapse. However, the present study showed that none of these pathological findings appeared to be related with renal relapse.
It is known that renal relapse most often occurs after reduction or cessation of immunosuppressive therapy. What has recently attracted the most attention in association with relapse is the maintenance treatment among therapeutic strategies [42]. Recently, the mainstream of maintenance regimen is AZP or MMF. However, comparative studies on effects of these two drugs are yielding different results in two studies [43,44]. In both of these two studies, maintenance treatment itself was found to be effective in flare prevention. When effects of the two drugs were compared, MMF showed a better effect than AZP in preventing renal relapse in the ALMS study [43], whereas there was no difference in efficacy between the two drugs in the MAINTAIN study [44]. Accordingly, in recent guidelines, MMF and AZP are recommended in equal positions for maintenance treatment [21]. Real-world data have revealed that discontinuation of immunosuppressive therapy is a predictor of renal relapse [35] and use of AZP as a maintenance treatment has been shown to increase renal relapse rate more than MMF [10,36].
Interestingly, as shown in Table 4, our data showed that the relapsed group received more immunosuppressive maintenance treatment and more statin as an adjuvant therapy. Even in treatment response, eGFR after 6 months of treatment was rather good in the relapse group. Although there was no significant difference in response to induction treatment or baseline disease severity between the two groups at the time of LN diagnosis, the relapsed group more tended to relapse more even after receiving more intensive maintenance treatment. Although the average duration of maintenance treatment was rather short at about 2 years, there was no significant difference in the duration of maintenance treatment between the two groups, suggesting that the currently used immunosuppressive maintenance treatment strategy is insufficient to effectively reduce renal relapse. In addition, recent guidelines recommend a maintenance duration of 3 to 5 years [21]. However, as described above, near half of patients were relapsed after 5 years (56.4 ± 49.4 mo). Therefore, we concluded that current treatment strategy is insufficient to prevent renal relapse and additional research for modification of current treatment strategy or novel treatment strategy is needed. Recently, results from randomized-controlled trials on belimumab add-on therapy were published [45,46], and these research trends support our conclusions. Regarding other treatment strategies, we did not find any statistical significance with respect to predictors of renal relapse suggested in previous studies, including delayed treatment initiation [30,32], achievement of early CR within 12 months [47], amount of proteinuria after 12 months [17,18], or time to CR [40].
Recently, one of the most important topics in LN treatment, especially maintenance treatment and relapse, is adherence to immunosuppressive agents [48]. We also considered this aspect, but there were limitations because it is a retrospective medical chart review study. To overcome these limitations, as we analyzed patients’ medical records, we excluded the cases when follow-up was interrupted to the extent that recurrence was likely to occur, or when medication was prescribed for less than 80% of the follow-up period due to notification that the patient did not take enough medication. However, since it cannot be confirmed whether all the prescribed drugs were actually taken, additional research is needed on this.
Finally, this study focused only on treatment until relapse in patients who relapsed after reaching CR. However, we think that the change in treatment after relapse and its results are also areas that clinicians should pay attention to. In our cohort, as a result of analyzing treatment changes in patients who relapsed, 40 patients (27.2%) were treated again with the initial induction regimen, 73 patients (49.7%) were treated with a different induction regimen, and 24 patients (16.3%) were treated only with maintenance treatment modification (data are not shown in Table). In the future, it would be interesting to analyze the outcomes according to the difference in treatment regimens in patients who relapsed.
This study was conducted by retrospectively analyzing medical records of cohort. There are some limitations. Because medical records were recorded in routine medical practice, there were some missing data that might have affected results of analysis. In addition, treatment manners were heterogenous depending on patients’ health conditions, socioeconomic status, and insurance problems. However, to the best of our knowledge, this study has the longest follow-up with the largest number of patients in a real-world setting. In addition, this is a single-center and single-ethnicity study with the advantage that characteristics of patients are homogenous.
In conclusion, this study showed that 38.2, 57.6, and 67.9% of Korean patients with LN who achieved CR relapsed within 5, 10, and 20 years, respectively. We found that only onset at a younger age was an independent predictor of renal relapse. In addition, patients with severe initial presentation regarding proteinuria and serum hypoalbuminemia tended to relapse more despite receiving immunosuppressive maintenance treatment for a sufficient period of time. Therefore, studies on more effective maintenance treatment regimens and duration are needed to reduce renal relapse.
1. Young-age onset of LN was an only independent predictor for renal relapse in Korean patients with LN who achieved CR.
2. The patients with severe proteinuria and serum hypoalbuminemia at diagnosis of LN tended to relapse more, despite of more intensive maintenance treatment with sufficient duration.
3. Studies on more effective maintenance treatment regimens and duration are needed to reduce renal relapse rate.
Notes
CRedit authorship contributions
Howook Jeon: investigation, data curation, formal analysis, writing - original draft; Jennifer Lee: resources, writing - review & editing; Su-Jin Moon: conceptualization, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, validation, writing - review & editing, visualization; Seung-Ki Kwok: conceptualization, methodology, resources, writing - review & editing; Ji Hyeon Ju: resources, writing - review & editing; Wan-Uk Kim: resources, writing - review & editing; Sung-Hwan Park: conceptualization, methodology, resources, writing - review & editing, supervision
Table 1
Comparison of clinical characteristics and laboratory findings at the diagnosis of LN depending on relapse
| Variable | Total (n = 296) | Relapse (n = 157) | Relapse free (n = 139) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 271/296 (91.6) | 144/157 (91.7) | 127/139 (91.4) | 0.913 |
| Age at SLE diagnosis, yr | 27.9 ± 10.2 | 26.3 ± 9.4 | 29.7 ± 10.8 | 0.006* |
| Age at LN diagnosis, yr | 29.8 ± 10.2 | 28.1 ± 9.3 | 31.7 ± 10.9 | 0.004* |
| SLE follow-up duration at the time of LN diagnosis, mo | 22.2 ± 39.8 | 21.1 ± 35.1 | 23.5 ± 44.5 | 0.744 |
| Delayed-onset LN | 176/296 (59.5) | 91/157 (58.0) | 85/139 (61.2) | 0.577 |
| Total follow-up duration from LN diagnosis, mo | 158.9 ± 91.4 | 172.5 ± 80.1 | 143.5 ± 100.7 | 0.002* |
| Total follow-up duration from CR, mo | 135.5 ± 85.9 | 150.6 ± 75.0 | 118.8 ± 94.5 | 0.001* |
| Medication at LN diagnosis | ||||
| Steroid | 80/91 (87.9) | 47/53 (88.7) | 33/38 (86.8) | 0.791 |
| Steroid dose, g/day | 10.02 ± 6.20 | 10.26 ± 6.95 | 9.69 ± 5.05 | 0.988 |
| Hydroxychloroquine | 51/91 (56.0) | 26/53 (49.1) | 25/38 (65.8) | 0.113 |
| SLEDAI | 18.4 ± 7.0 | 17.4 ± 5.2 | 19.9 ± 9.2 | 0.343 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 22.03 ± 3.31 | 22.23 ± 3.16 | 21.76 ± 3.51 | 0.388 |
| Hypertension | 42/212 (19.8) | 20/116 (17.2) | 22/96 (22.9) | 0.302 |
| Hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL | 98/238 (41.2) | 56/127 (44.1) | 42/111 (37.8) | 0.328 |
| Platelets less than 100,000/μL | 43/238 (18.1) | 21/126 (16.7) | 22/112 (19.6) | 0.551 |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | 1.02 ± 0.68 | 1.03 ± 0.79 | 1.01 ± 0.54 | 0.358 |
| Serum eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 88.9 ± 34.1 | 91.7 ± 35.5 | 85.9 ± 32.5 | 0.189 |
| Acute renal dysfunction at LN onset, eGFR < 60 | 48/240 (20.0) | 25/125 (20.0) | 23/115 (20.0) | > 0.999 |
| Severe renal dysfunction at LN onset, eGFR < 30 | 10/240 (4.2) | 5/125 (4.0) | 5/115 (4.3) | > 0.999 |
| Urinary casts | 97/227 (42.7) | 55/118 (46.6) | 42/109 (38.5) | 0.219 |
| Proteinuria, g/day or PC ratio | 5.4250 ± 5.8261 | 6.050 ± 6.8927 | 4.7789 ± 4.4020 | 0.101 |
| Nephrotic range proteinuria | 126/241 (52.3) | 68/123 (55.3) | 58/118 (49.2) | 0.341 |
| Proteinuria over 6 g | 72/240 (30.0) | 46/122 (37.7) | 26/118 (22.0) | 0.008* |
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 2.81 ± 0.74 | 2.74 ± 0.77 | 2.90 ± 0.69 | 0.115 |
| Hypoalbuminemia, less than 3.5 g/dL | 185/235 (78.7) | 99/123 (80.5) | 86/112 (76.8) | 0.489 |
| Clinically significant hypoalbuminemia, less than 2.5 g/dL | 77/235 (32.8) | 46/123 (37.4) | 31/112 (27.7) | 0.113 |
| Albumin less than 2.0 g/dL | 34/235 (14.5) | 25/123 (20.3) | 9/112 (8.0) | 0.007* |
| Serum uric acid, mg/dL | 6.35 ± 2.28 | 6.35 ± 2.30 | 6.34 ± 2.27 | 0.964 |
Table 2
Comparison of immunological laboratory findings at the diagnosis of lupus nephritis depending on relapse
| Variable | Total (n = 296) | Relapse (n = 157) | Relapse free (n = 139) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3, mg/dL | 43.28 ± 24.90 | 43.46 ± 23.37 | 43.08 ± 26.59 | 0.624 |
| C4, mg/dL | 9.99 ± 7.43 | 9.47 ± 6.44 | 10.56 ± 8.40 | 0.751 |
| ANA positivity | 273/283 (96.5) | 147/151 (97.4) | 126/132 (95.5) | 0.523 |
| Anti-dsDNA Ab positivity | 198/215 (92.1) | 107/114 (93.9) | 91/101 (90.1) | 0.308 |
| Anti-dsDNA Ab titer, far assay, IU/mL | 289.42 ± 344.84 | 243.72 ± 314.89 | 347.08 ± 357.20 | 0.322 |
| Anti-Sm Ab positivity | 67/207 (32.4) | 43/114 (37.7) | 24/93 (25.8) | 0.068 |
| Anti-Ro Ab positivity | 129/220 (58.6) | 70/122 (57.4) | 59/98 (60.2) | 0.672 |
| Anti-La Ab positivity | 43/198 (21.7) | 27/110 (24.5) | 16/88 (18.2) | 0.281 |
| Anti-RNP Ab positivity | 95/191 (49.7) | 54/107 (50.5) | 41/84 (48.8) | 0.820 |
| Anti-phospholipid Ab positivity | 101/247 (40.9) | 53/139 (38.1) | 48/108 (44.4) | 0.317 |
| Anti-β2-glycoprotein Ab positivity | 48/244 (19.7) | 24/138 (17.4) | 24/106 (22.6) | 0.306 |
| Anti-cardiolipin Ab positivity | 70/285 (24.6) | 40/153 (26.1) | 30/132 (22.7) | 0.504 |
| Lupus anticoagulant positivity | 33/274 (12.0) | 24/154 (15.6) | 9/120 (7.5) | 0.041* |
Table 3
Comparision of pathological findings at the diagnosis of lupus nephritis depending on relapse
Table 4
Comparison of therapeutic regimens and treatment response depending on relapse
| Variable | Total (n = 296) | Relapse (n = 157) | Relapse free (n = 139) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delay time from diagnosis of LN to treatment, mo | 2.6 ± 8.9 | 2.9 ± 10.4 | 2.3 ± 6.7 | 0.630 |
| Induction treatment type | 0.604 | |||
| Steroid only | 93/281 (33.1) | 50/151 (33.1) | 43/130 (33.1) | |
| Cyclophosphamide | 132/281 (47.0) | 73/151 (48.3) | 59/130 (45.4) | |
| MMF | 40/281 (14.2) | 18/151 (11.9) | 22/130 (16.9) | |
| CNIs | 16/281 (5.7) | 10/151 (6.6) | 6/130 (4.6) | |
| Maintenance treatment type | 0.049* | |||
| None | 23/262 (8.8) | 8/137 (5.8) | 15/125 (12.0) | |
| Steroid only | 55/262 (21.0) | 23/137 (16.8) | 32/125 (25.6) | |
| Cyclophosphamide | 50/262 (19.1) | 29/137 (21.2) | 21/125 (16.8) | |
| MMF | 57/262 (21.8) | 28/137 (20.4) | 29/125 (16.8) | |
| AZP | 61/262 (23.3) | 37/137 (27.0) | 24/125 (19.2) | |
| CNIs | 16/262 (6.1) | 12/137 (8.8) | 4/125 (3.2) | |
| Cytotoxic maintenance treatment | 184/262 (70.2) | 106/137 (77.4) | 78/125 (62.4) | 0.008* |
| Maintenance treatment duration, mo | 22.0 ± 25.0 | 19.4 ± 22.1 | 24.6 ± 27.4 | 0.505 |
| Steroid treatment duration (tapered to 5 mg/day), mo | 30.4 ± 33.6 | 28.1 ± 28.5 | 32.7 ± 37.9 | 0.796 |
| Steroid hold | 68/232 (29.3) | 27/114 (23.7) | 41/118 (34.7) | 0.064 |
| Adjuvant treatment | ||||
| ARB or ACEi | 113/227 (49.8) | 60/115 (52.2) | 53/112 (47.3) | 0.465 |
| Statin | 53/227 (23.3) | 34/115 (29.6) | 19/112 (17.0) | 0.025* |
| HCQ | 113/227 (4.8) | 58/115 (50.4) | 55/112 (49.1) | 0.841 |
| Treatment response at 6 months | 0.555 | |||
| CR | 142/260 (54.6) | 77/135 (57.0) | 65/125 (52.0) | |
| PR | 39/260 (15.0) | 21/135 (15.6) | 18/125 (14.4) | |
| NR | 79/260 (30.4) | 37/135 (27.4) | 42/125 (33.6) | |
| Serum eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 96.4 ± 26.9 | 100.5 ± 27.5 | 91.7 ± 25.4 | 0.017* |
| Proteinuria, g/24 h | 1.5957 ± 4.3749 | 1.9375 ± 5.7858 | 1.2081 ± 2.8520 | 0.739 |
| Treatment response at 12 months | 0.758 | |||
| CR | 163/257 (63.4) | 88/136 (64.7) | 75/121 (62.0) | |
| PR | 38/257 (14.8) | 18/136 (13.2) | 20/121 (16.5) | |
| NR | 56/257 (21.8) | 30/136 (22.1) | 26/121 (21.5) | |
| Serum eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 101.3 ± 32.5 | 104.7 ± 34.5 | 97.5 ± 29.8 | 0.100 |
| Proteinuria, g/24 h | 1.5502 ± 4.4654 | 1.1659 ± 2.2486 | 2.0776 ± 6.3621 | 0.768 |
| Time to CR, mo | 19.1 ± 26.7 | 16.3 ± 23.2 | 22.2 ± 29.9 | 0.120 |
ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin-receptor blocker; AZP, azathioprine; CNIs, calcineurin inhibitors; CR, complete response; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HCQ, hydroxychloroquine; LN, lupus nephritis; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; NR, no response; PR, partial response.
Table 5
Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards analyses of the predictors of relapse in patients with LN
| Variable | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||
| HR (95% CI) | p value | HR (95% CI) | p value | |
| Age at SLE, 10 yr | 0.781 (0.650–0.939) | 0.008* | ||
|
|
||||
| Age at LN, 10 yr | 0.779 (0.650–0.933) | 0.007* | 0.779 (0.650–0.933) | 0.007* |
|
|
||||
| Proteinuria over 6 g | 1.322 (0.912–1.915) | 0.140 | ||
|
|
||||
| Albumin less than 2.0 g/dL | 1.361 (0.870–2.130) | 0.177 | ||
|
|
||||
| Lupus anticoagulant positivity | 1.196 (0.744–1.923) | 0.460 | ||
REFERENCES
1. Fasano S, Milone A, Nicoletti GF, Isenberg DA, Ciccia F. Precision medicine in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2023;19:331–342.



2. Hocaoğlu M, Valenzuela-Almada MO, Dabit JY, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and mortality of lupus nephritis: a population-based study over four decades using the lupus midwest network. Arthritis Rheumatol 2023;75:567–573.


3. Danila MI, Pons-Estel GJ, Zhang J, Vilá LM, Reveille JD, Alarcón GS. Renal damage is the most important predictor of mortality within the damage index: data from LUMINA LXIV, a multiethnic US cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48:542–545.



5. Yap DY, Tang CS, Ma MK, Lam MF, Chan TM. Survival analysis and causes of mortality in patients with lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012;27:3248–3254.


6. Moroni G, Quaglini S, Maccario M, Banfi G, Ponticelli C. “Nephritic flares” are predictors of bad long-term renal outcome in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 1996;50:2047–2053.


7. Mosca M, Bencivelli W, Neri R, et al. Renal flares in 91 SLE patients with diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2002;61:1502–1509.


8. El Hachmi M, Jadoul M, Lefèbvre C, Depresseux G, Houssiau FA. Relapses of lupus nephritis: incidence, risk factors, serology and impact on outcome. Lupus 2003;12:692–696.


9. Moroni G, Quaglini S, Gallelli B, Banfi G, Messa P, Ponticelli C. The long-term outcome of 93 patients with proliferative lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2007;22:2531–2539.


10. Mejía-Vilet JM, Córdova-Sánchez BM, Arreola-Guerra JM, Morales-Buenrostro LE, Uribe-Uribe NO, Correa-Rotter R. Renal flare prediction and prognosis in lupus nephritis Hispanic patients. Lupus 2016;25:315–324.



11. Mok CC, Ying KY, Tang S, et al. Predictors and outcome of renal flares after successful cyclophosphamide treatment for diffuse proliferative lupus glomerulonephritis. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:2559–2568.


12. Weinmann-Menke J, Kraus D. Care about the flare: the importance of avoiding lupus nephritis recurrence. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2023;38:800–802.



13. Perez-Arias AA, Márquez-Macedo SE, Pena-Vizcarra OR, et al. The influence of repeated flares in response to therapy and prognosis in lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2023;38:884–893.



14. Moroni G, Gallelli B, Quaglini S, et al. Withdrawal of therapy in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis: long-term follow-up. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006;21:1541–1548.


15. Yap DYH, Tang C, Ma MKM, et al. Longterm data on disease flares in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis in recent years. J Rheumatol 2017;44:1375–1383.


16. Moon SJ, Park HS, Kwok SK, et al. Predictors of renal relapse in Korean patients with lupus nephritis who achieved remission six months following induction therapy. Lupus 2013;22:527–537.



17. Ligtenberg G, Arends S, Stegeman CA, de Leeuw K. Predictors of renal flares and long-term renal outcome in patients with lupus nephritis: results from daily clinical practice. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2022;40:33–38.


18. Kapsia E, Marinaki S, Michelakis I, et al. Predictors of early response, flares, and long-term adverse renal outcomes in proliferative lupus nephritis: a 100-month median follow-up of an inception cohort. J Clin Med 2022;11:5017.



19. Isenberg D, Appel GB, Contreras G, et al. Influence of race/ ethnicity on response to lupus nephritis treatment: the ALMS study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010;49:128–140.



20. Mohan S, Radhakrishnan J. Geographical variation in the response of lupus nephritis to mycophenolate mofetil induction therapy. Clin Nephrol 2011;75:233–241.


21. Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Cheema K, et al. 2019 Update of the Joint European League Against Rheumatism and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:713–723.

22. Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1997;40:1725.


23. Moroni G, Gatto M, Tamborini F, et al. Lack of EULAR/ERA-EDTA response at 1 year predicts poor long-term renal outcome in patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:1077–1083.


25. Churg J, Sobin LH. Renal Disease: Classification and Atlas of Glomerular Diseases. Tokyo: Igaku-Shoin, 1982.
26. Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, et al.; International Society of Nephrology Working Group on the Classification of Lupus Nephritis; Renal Pathology Society Working Group on the Classification of Lupus Nephritis. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int 2004;65:521–530.


27. Austin HA 3rd, Muenz LR, Joyce KM, et al. Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. Contribution of renal histologic data. Am J Med 1983;75:382–391.

28. Illei GG, Takada K, Parkin D, et al. Renal flares are common in patients with severe proliferative lupus nephritis treated with pulse immunosuppressive therapy: long-term followup of a cohort of 145 patients participating in randomized controlled studies. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:995–1002.


29. Chen YE, Korbet SM, Katz RS, Schwartz MM, Lewis EJ, Collaborative Study Group. Value of a complete or partial remission in severe lupus nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2008;3:46–53.



30. So MW, Koo BS, Kim YG, Lee CK, Yoo B. Predictive value of remission status after 6 months induction therapy in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis: a retrospective analysis. Clin Rheumatol 2011;30:1399–1405.



31. Boumpas DT, Austin HA 3rd, Vaughn EM, et al. Controlled trial of pulse methylprednisolone versus two regimens of pulse cyclophosphamide in severe lupus nephritis. Lancet 1992;340:741–745.


32. Ciruelo E, de la Cruz J, López I, Gómez-Reino JJ. Cumulative rate of relapse of lupus nephritis after successful treatment with cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum 1996;39:2028–2034.


33. Houssiau FA, Vasconcelos C, D’Cruz D, et al. Immunosuppressive therapy in lupus nephritis: the Euro-Lupus Nephritis Trial, a randomized trial of low-dose versus high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:2121–2131.


34. Mok CC, Ho CT, Chan KW, Lau CS, Wong RW. Outcome and prognostic indicators of diffuse proliferative lupus glomerulonephritis treated with sequential oral cyclophosphamide and azathioprine. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:1003–1013.


35. Hajji M, Harzallah A, Kaaroud H, Barbouch S, Hamida FB, Abdallah TB. Factors associated with relapse of lupus nephritis: A single center study of 249 cases. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2017;28:1349–1355.


36. Barber CE, Geldenhuys L, Hanly JG. Sustained remission of lupus nephritis. Lupus 2006;15:94–101.



37. Cortés-Hernández J, Torres-Salido MT, Medrano AS, Tarrés MV, Ordi-Ros J. Long-term outcomes--mycophenolate mofetil treatment for lupus nephritis with addition of tacrolimus for resistant cases. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2010;25:3939–3948.


38. Suzuki E, Yashiro-Furuya M, Temmoku J, et al. Comparison of renal remission and relapse-free rate in initial- and delayed-onset lupus nephritis. Int J Rheum Dis 2021;24:1500–1509.




39. Cortés-Hernández J, Ordi-Ros J, Labrador M, et al. Predictors of poor renal outcome in patients with lupus nephritis treated with combined pulses of cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone. Lupus 2003;12:287–296.



40. Ioannidis JP, Boki KA, Katsorida ME, et al. Remission, relapse, and re-remission of proliferative lupus nephritis treated with cyclophosphamide. Kidney Int 2000;57:258–264.


41. Kwon OC, Cho YM, Oh JS, et al. Renal flare in class V lupus nephritis: increased risk in patients with tubulointerstitial lesions. Rheumatol Int 2019;39:2061–2067.



42. Sprangers B, Monahan M, Appel GB. Diagnosis and treatment of lupus nephritis flares--an update. Nat Rev Nephrol 2012;8:709–717.



43. Dooley MA, Jayne D, Ginzler EM, et al.; ALMS Group. Mycophenolate versus azathioprine as maintenance therapy for lupus nephritis. N Engl J Med 2011;365:1886–1895.


44. Houssiau FA, D’Cruz D, Sangle S, et al.; MAINTAIN Nephritis Trial Group. Azathioprine versus mycophenolate mofetil for long-term immunosuppression in lupus nephritis: results from the MAINTAIN Nephritis Trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:2083–2089.



45. Furie R, Rovin BH, Houssiau F, et al. Two-year, randomized, controlled trial of belimumab in lupus nephritis. N Engl J Med 2020;383:1117–1128.


46. Atisha-Fregoso Y, Malkiel S, Harris KM, et al. Phase II randomized trial of rituximab plus cyclophosphamide followed by belimumab for the treatment of lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2021;73:121–131.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print