|
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 30(3); 2015 > Article |
|
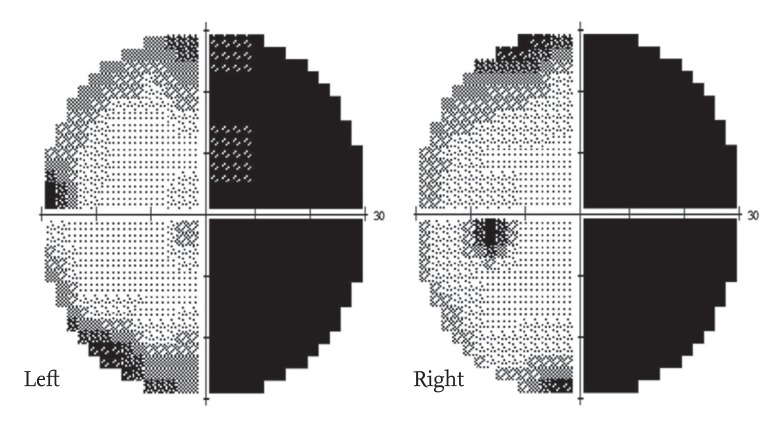
A 49-year-old male with a 10-year history of Behcet's disease (BD) presented with sudden visual field defects in both eyes the first occurred when walking. Laboratory testing revealed an elevated serum C-reactive protein (1.3 mg/dL) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (47 mm/hr). The Humphrey visual field test showed right homonymous hemianopia (Fig. 1), while no abnormal findings were identified on fundal examination. Suspecting homonymous hemianopia, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed; T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MRI showed circumferential high-intensity lesions of the left lateral geniculate body (Fig. 2A). Consequently, he was diagnosed with acute neuro-BD and given steroid pulse therapy (1 g/day) for 3 days, followed by highdose prednisolone (1 mg/kg/day) and a cyclophosphamide pulse (750 mg/day). The lesions in the lateral geniculate body were reduced on MRI taken 2 weeks after treatment (Fig. 2B), but the homonymous hemianopia remained nearly unchanged. We plan to administer two cyclophosphamide pulse treatments per month. Ocular manifestations are one of the main features of BD, especially uveitis and retinal vasculitis that progressively damage the vision. Homonymous hemianopia with hemianopic visual field loss on the same side in both eyes is extremely rare in BD. The pathogenesis of the lesions in the geniculate bodies in these cases is believed to be related to underlying vascular involvement of the inflammation. Early immunosuppressant use is necessary; intravenous cyclophosphamide combined with corticosteroids can improve the prognosis. When patients with BD have visual defects, clinicians should consider brain MRI to detect cerebral lesions, as well as a fundal examination.
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 1 Scopus
- 9,730 View
- 107 Download
- Related articles
-
Endoscopic unusual appearance of stomach in a patient with Crohn’s disease2023 March;38(2)
Nutritional management in patients with chronic kidney disease2020 November;35(6)
Atypical cutaneous features in a patient with adult-onset Still’s disease2021 May;36(3)
Unusual milia-type intradermal tophi in a patient with gout2020 May;35(3)




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print