|
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 40(4); 2025 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
Methods
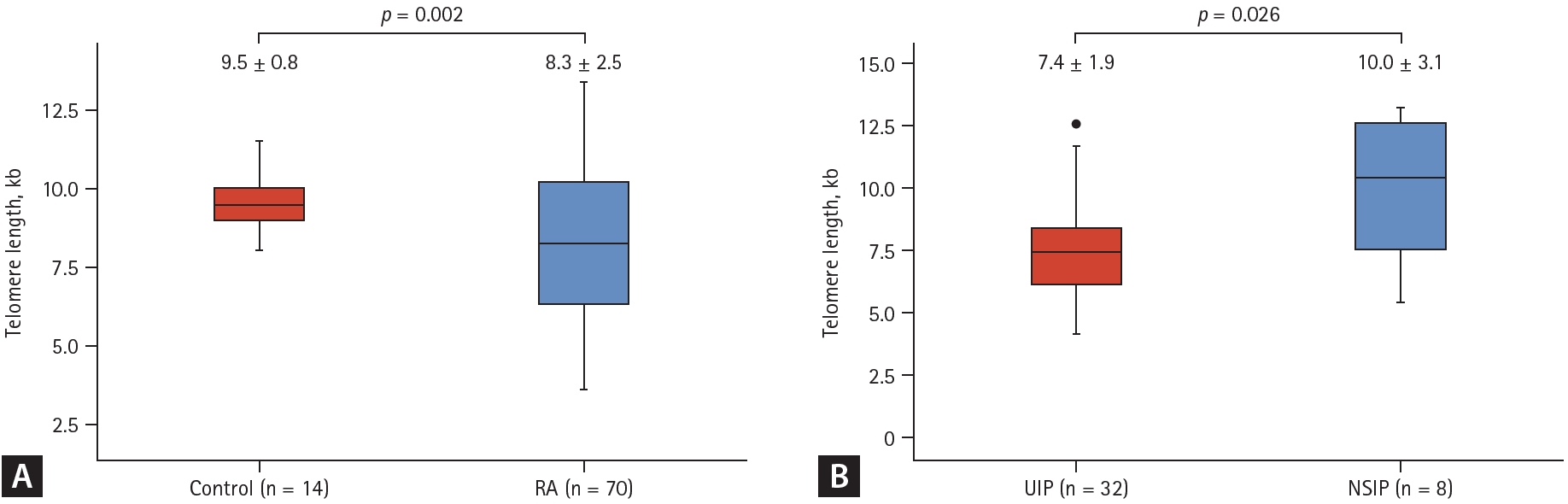
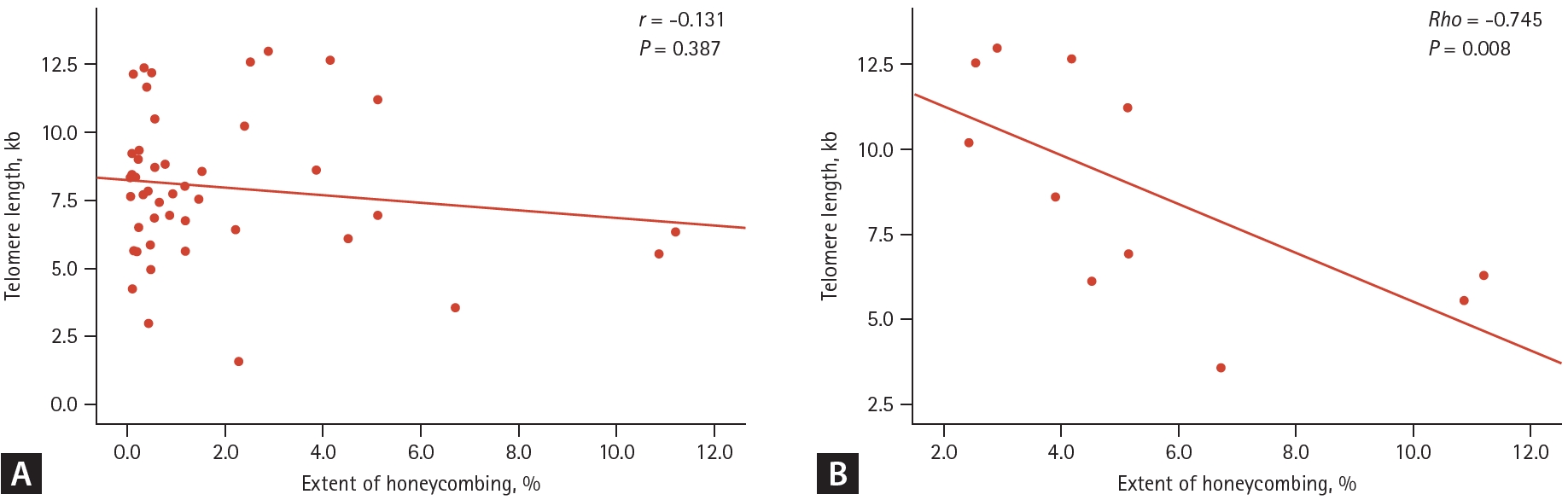
Results
Notes
Figure┬Ā1.
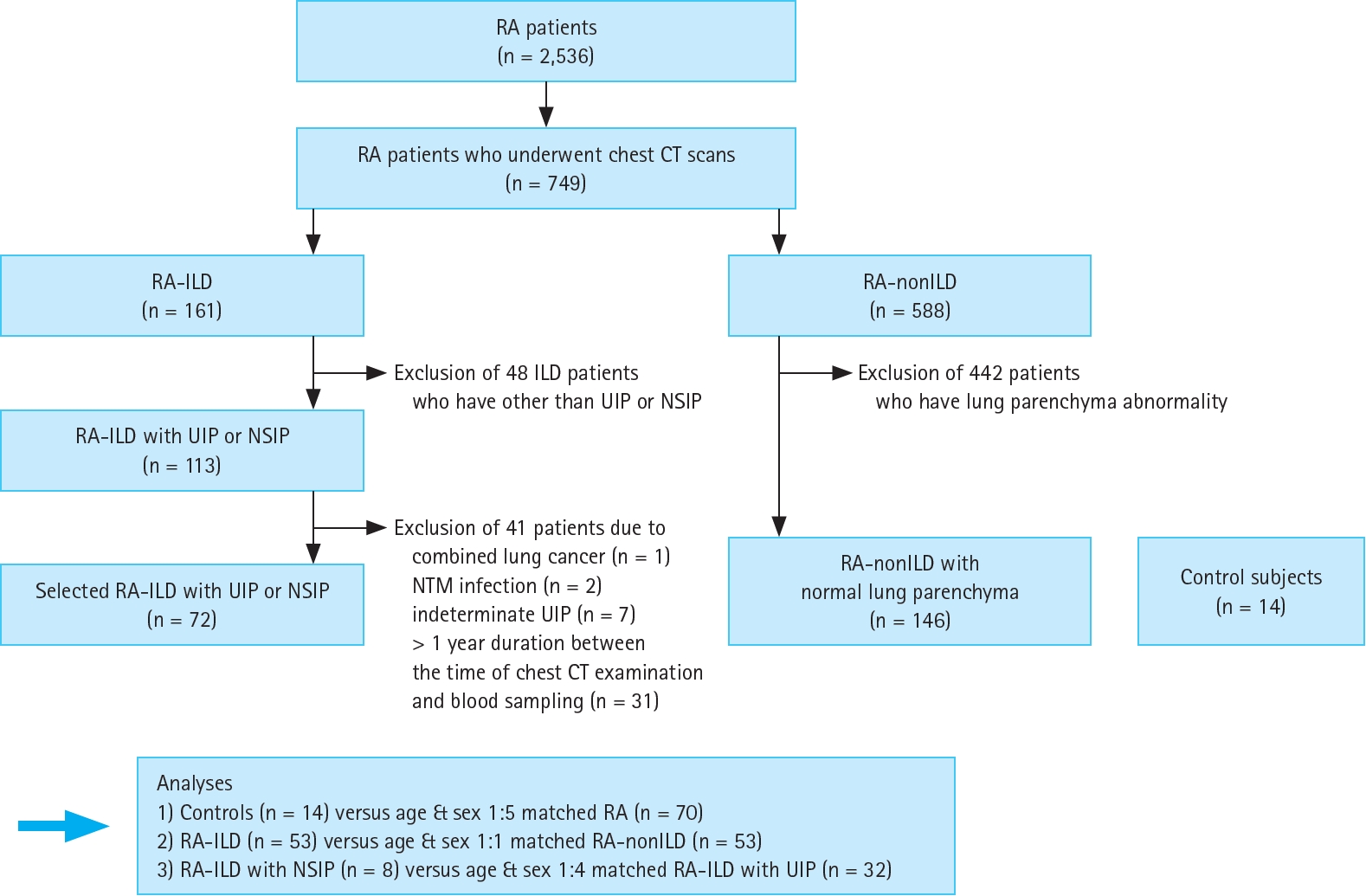
Figure┬Ā2.
Figure┬Ā3.
Table┬Ā1.
Values are presented as mean ┬▒ standard deviation or number (%).
RA, rheumatoid arthritis; ILD, interstitial lung disease; RF, rheumatoid factor; CCP, cyclic citrullinated peptide; ab, antibody; DAS, disease activity score; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C-reactive protein; DMARDs, disease modifying antirheumatic drugs; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; FVC, forced vital capacity; DLCO, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide.
Table┬Ā2.
| Variable | RA, total (n = 106) | RA-ILD (n = 53) | RA-nonILD (n = 53) | p valuea) |
RA-ILD subtype |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIP (n = 32) | NSIP (n = 8) | p value | |||||
| TL (kb) | 8.0 ┬▒ 2.6 | 8.2 ┬▒ 2.8 | 7.7 ┬▒ 2.4 | 0.271 | 7.4 ┬▒ 1.9 | 10.0 ┬▒ 3.1 | 0.026 |
| TERC | |||||||
| ŌĆāGG | 51 (48.1) | 24 (45.3) | 27 (50.9) | 0.740 | 15 (46.9) | 4 (50.0) | 0.846 |
| ŌĆāGC | 49 (46.2) | 25 (47.2) | 24 (45.3) | 15 (46.9) | 3 (37.5) | ||
| ŌĆāCC | 6 (5.7) | 4 (7.5) | 2 (3.8) | 2 (6.3) | 1 (12.5) | ||
| TERT | |||||||
| ŌĆāCC | 50 (47.2) | 28 (52.8) | 22 (41.5) | 0.115 | 15 (46.9) | 4 (50.0) | 1.000 |
| ŌĆāCA | 44 (41.5) | 17 (32.1) | 27 (50.9) | 13 (40.6) | 3 (37.5) | ||
| ŌĆāAA | 12 (11.3) | 8 (15.1) | 4 (7.5) | 4 (12.5) | 1 (12.5) | ||
Values are presented as mean ┬▒ standard deviation or number (%).
RA, rheumatoid arthritis; ILD, interstitial lung disease; UIP, usual interstitial pneumonia; NSIP, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; TL, telomere length; TERC, telomerase ribonucleic acid component; TERT, telomerase reverse transcriptase.
Table┬Ā3.
| Variable |
Univariate linear regression |
Multiple linear regression |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient (╬▓) | S.E. | p value | Coefficient (╬▓) | S.E. | p value | |
| Age at sampling (yr) | -0.14 | 0.04 | 0.0004 | -0.08 | 0.03 | 0.011 |
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | -0.07 | 0.04 | 0.051 | - | - | - |
| Sex, women | -0.01 | 0.77 | 0.985 | - | - | - |
| Smoking, ever | -0.08 | 0.78 | 0.917 | - | - | - |
| RF positivity | 1.57 | 1.12 | 0.168 | - | - | - |
| RF titer (IU/mL) | 1.57 | 1.12 | 0.168 | - | - | - |
| Anti-CCP antibody | -1.75 | 1.41 | 0.222 | - | - | - |
| Anti-CCP antibody titer (U/mL) | -3.6 ├Ś 10-5 | 0.00 | 0.862 | - | - | - |
| DAS28-ESR | -0.46 | 0.27 | 0.093 | - | - | - |
| DAS28-CRP | -0.71 | 0.28 | 0.017 | -0.60 | 0.24 | 0.018 |
| DLCO | -0.06 | 0.02 | 0.004 | -0.04 | 0.02 | 0.053 |
| UIPa) | -2.57 | 0.85 | 0.004 | -1.38 | 0.63 | 0.038 |
RA, rheumatoid arthritis; ILD, interstitial lung disease; S.E., standard error; RF, rheumatoid factor; CCP, cyclic citrullinated peptide; DAS, disease activity score; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C-reactive protein; DLCO, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide, UIP, usual interstitial pneumonia.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement table 1
Supplement table 1 Print
Print