1. Wilson PW, Castelli WP, Kannel WB. Coronary risk prediction in adults (the Framingham Heart Study). Am J Cardiol 1987;59:91GŌĆō94G.


2. Verschuren WM, Jacobs DR, Bloemberg BP, et al. Serum total cholesterol and long-term coronary heart disease mortality in different cultures. Twenty-five-year follow-up of the seven countries study. JAMA 1995;274:131ŌĆō136.


8. Prospective Studies Collaboration. Lewington S, Whitlock G, Clarke R, et al. Blood cholesterol and vascular mortality by age, sex, and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of individual data from 61 prospective studies with 55,000 vascular deaths. Lancet 2007;370:1829ŌĆō1839.


9. Kim NH, Lee J, Chon S, et al. Study design and protocol for a randomized controlled trial to assess long-term efficacy and safety of a triple combination of ezetimibe, fenofibrate, and moderate-intensity statin in patients with type 2 diabetes and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors (ENSEMBLE). Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2024;39:722ŌĆō731.


14. Iseki K, Yamazato M, Tozawa M, Takishita S. Hypocholesterolemia is a significant predictor of death in a cohort of chronic hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 2002;61:1887ŌĆō1893.


15. Wanner C, Krane V, M├żrz W, et al.; German Diabetes and Dialysis Study Investigators. Atorvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 2005;353:238ŌĆō248.


16. Fellstr├Čm BC, Jardine AG, Schmieder RE, et al.; AURORA Study Group. Rosuvastatin and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 2009;360:1395ŌĆō1407.

17. Wanner C, Tonelli M, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Lipid Guideline Development Work Group Members. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Lipid Management in CKD: summary of recommendation statements and clinical approach to the patient. Kidney Int 2014;85:1303ŌĆō1309.


18. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2024;105:S117ŌĆōS314.


19. Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;73:3168ŌĆō3209.

20. Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, et al.; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J 2020;41:111ŌĆō188.

21. Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline of the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis. Korean guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia. 5th ed. Anyang: Academya, 2022.
22. Korean Society of Nephrology. Korean Society of Nephrology 2023 practical recommendations for the management of diabetic kidney disease [Internet] Seoul: Korean Society of Nephrology, 2023. [cited 2025 Mar 18]. Available from:
https://ksn.or.kr/bbs/?code=guideline_k.
25. Akmal M, Kasim SE, Soliman AR, Massry SG. Excess parathyroid hormone adversely affects lipid metabolism in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 1990;37:854ŌĆō858.


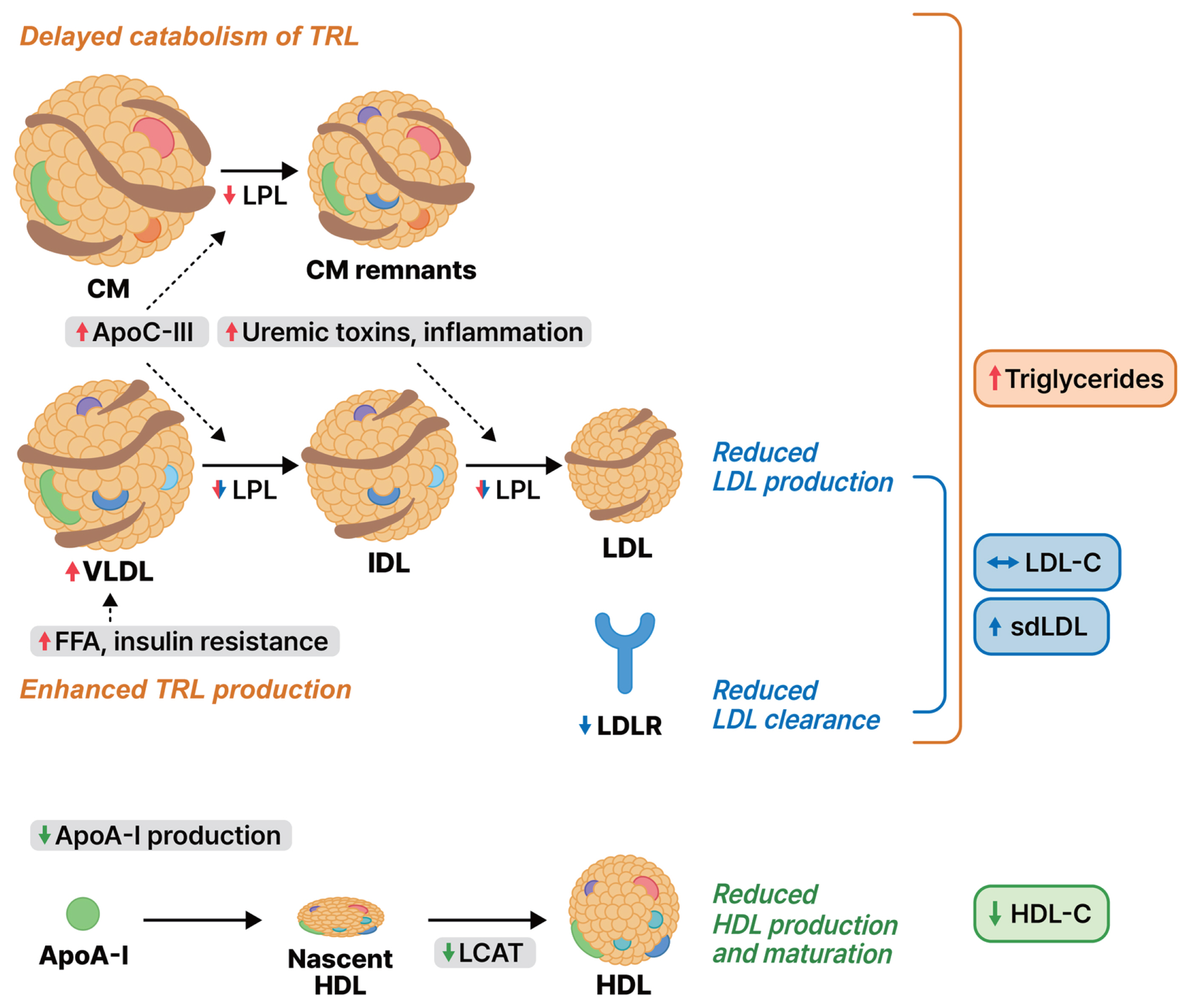
26. Vaziri ND, Liang K. Down-regulation of tissue lipoprotein lipase expression in experimental chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 1996;50:1928ŌĆō1935.


28. Kim C, Vaziri ND. Down-regulation of hepatic LDL receptor-related protein (LRP) in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 2005;67:1028ŌĆō1032.


30. Kaysen GA. Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in chronic kidney disease. J Ren Nutr 2009;19:73ŌĆō77.


32. Chu M, Wang AY, Chan IH, Chui SH, Lam CW. Serum small-dense LDL abnormalities in chronic renal disease patients. Br J Biomed Sci 2012;69:99ŌĆō102.


35. Cholesterol Treatment Trialists' (CTT) Collaboration. Herrington WG, Emberson J, Mihaylova B, et al. Impact of renal function on the effects of LDL cholesterol lowering with statin-based regimens: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from 28 randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2016;4:829ŌĆō839.


37. Kilpatrick RD, McAllister CJ, Kovesdy CP, Derose SF, Kopple JD, Kalantar-Zadeh K. Association between serum lipids and survival in hemodialysis patients and impact of race. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007;18:293ŌĆō303.


39. Takahashi O, Glasziou PP, Perera R, et al. Lipid re-screening: what is the best measure and interval? Heart 2010;96:448ŌĆō452.


43. Su X, Zhang L, Lv J, et al. Effect of statins on kidney disease outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 2016;67:881ŌĆō892.


44. Haynes R, Lewis D, Emberson J, et al.; SHARP Collaborative Group; SHARP Collaborative Group. Effects of lowering LDL cholesterol on progression of kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2014;25:1825ŌĆō1833.


45. Baigent C, Landray MJ, Reith C, et al.; SHARP Investigators. The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with simvastatin plus ezetimibe in patients with chronic kidney disease (Study of Heart and Renal Protection): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2011;377:2181ŌĆō2192.


46. Barylski M, Nikfar S, Mikhailidis DP, et al.; Lipid and Blood Pressure Meta-Analysis Collaboration Group. Statins decrease all-cause mortality only in CKD patients not requiring dialysis therapy--a meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials involving 21,295 participants. Pharmacol Res 2013;72:35ŌĆō44.


49. Tonelli M, Muntner P, Lloyd A, et al.; Alberta Kidney Disease Network. Risk of coronary events in people with chronic kidney disease compared with those with diabetes: a population-level cohort study. Lancet 2012;380:807ŌĆō814.


50. Saito Y, Goto Y, Nakaya N, et al. Dose-dependent hypolipidemic effect of an inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, pravastatin (CS-514), in hypercholesterolemic subjects. A double blind test. Atherosclerosis 1988;72:205ŌĆō211.


51. Saito Y, Goto Y, Dane A, Strutt K, Raza A. Randomized dose-response study of rosuvastatin in Japanese patients with hypercholesterolemia. J Atheroscler Thromb 2003;10:329ŌĆō336.


52. Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 1998;32:S112ŌĆōS119.


55. Holdaas H, Fellstr├Čm B, Jardine AG, et al.; Assessment of LEscol in Renal Transplantation (ALERT) Study Investigators. Effect of fluvastatin on cardiac outcomes in renal transplant recipients: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2003;361:2024ŌĆō2031.


56. Holdaas H, Fellstr├Čm B, Cole E, et al.; Assessment of LEscol in Renal Transplantation (ALERT) Study Investigators. Long-term cardiac outcomes in renal transplant recipients receiving fluvastatin: the ALERT extension study. Am J Transplant 2005;5:2929ŌĆō2936.


57. Page RL 2nd, Miller GG, Lindenfeld J. Drug therapy in the heart transplant recipient: part IV: drug-drug interactions. Circulation 2005;111:230ŌĆō239.


58. Sabatine MS, Giugliano RP, Keech AC, et al.; FOURIER Steering Committee and Investigators. Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1713ŌĆō1722.


59. Schwartz GG, Steg PG, Szarek M, et al.; ODYSSEY OUTCOMES Committees and Investigators. Alirocumab and cardiovascular outcomes after acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med 2018;379:2097ŌĆō2107.


60. Charytan DM, Sabatine MS, Pedersen TR, et al.; FOURIER Steering Committee and Investigators. Efficacy and safety of evolocumab in chronic kidney disease in the FOURIER trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;73:2961ŌĆō2970.


61. Toth PP, Dwyer JP, Cannon CP, et al. Efficacy and safety of lipid lowering by alirocumab in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2018;93:1397ŌĆō1408.


62. Keech A, Simes RJ, Barter P, et al.; FIELD study investigators. Effects of long-term fenofibrate therapy on cardiovascular events in 9795 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the FIELD study): randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005;366:1849ŌĆō1861.


66. Jun M, Zhu B, Tonelli M, et al. Effects of fibrates in kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;60:2061ŌĆō2071.

67. Jenkins AJ, O'Connell RL, Januszewski AS, et al.; FIELD Trial Study Group. Not enough known about fenofibrate's kidney effects in people with Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2024;210:111612.


69. Bhatt DL, Steg PG, Miller M, et al.; REDUCE-IT Investigators. Cardiovascular risk reduction with icosapent ethyl for hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med 2019;380:11ŌĆō22.


71. Nicholls SJ, Lincoff AM, Garcia M, et al. Effect of high-dose omega-3 fatty acids vs corn oil on major adverse cardiovascular events in patients at high cardiovascular risk: the STRENGTH randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2020;324:2268ŌĆō2280.


72. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2022 clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2022;102:S1ŌĆōS127.







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print