|
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 40(6); 2025 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
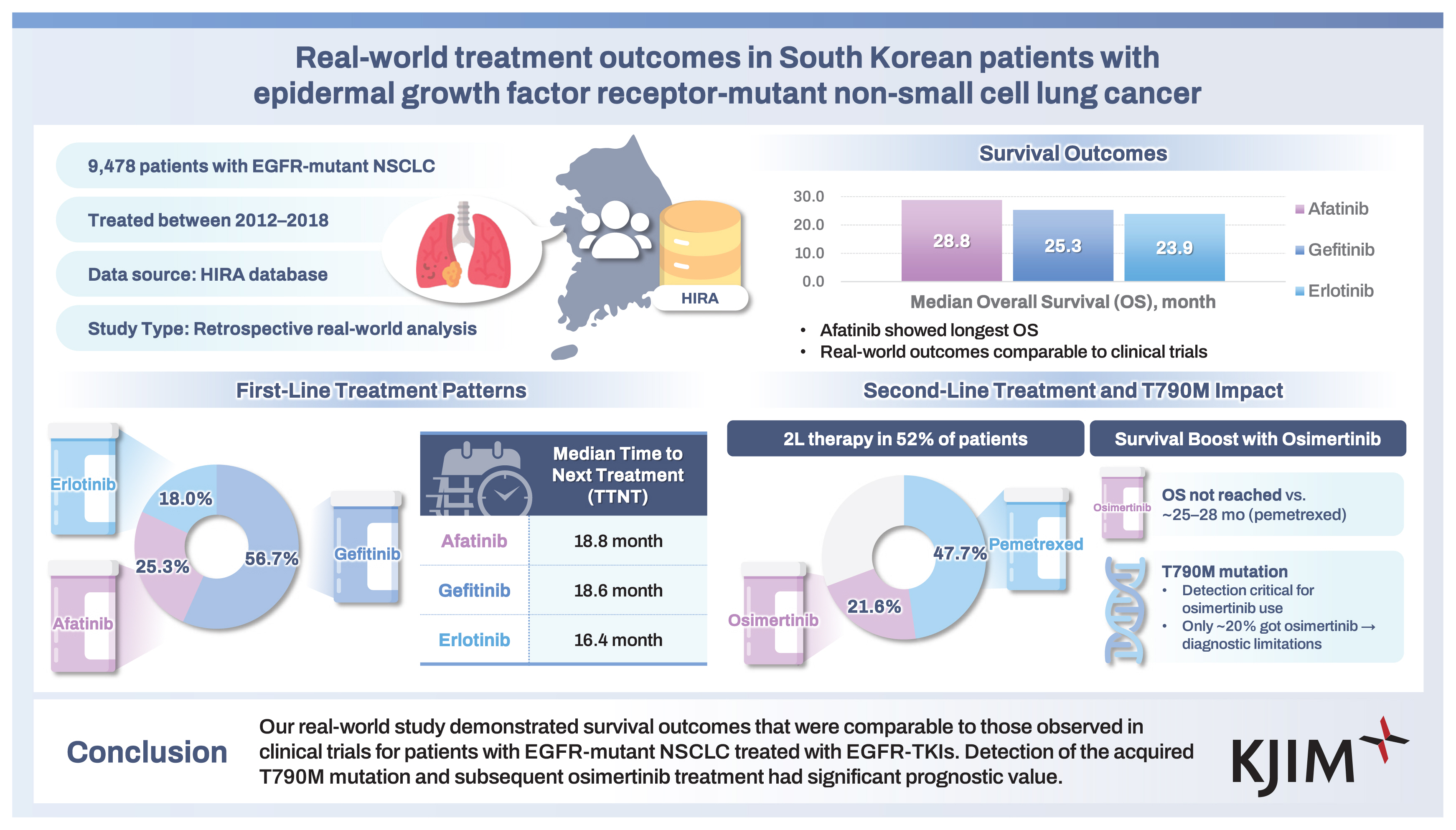
This study aimed to assess the real-world treatment outcomes in South Korean patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) receiving first-line (1L) EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Methods
We used the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service database, which includes the data of a large proportion of the Korean population. Patients with EGFR-positive NSCLC who received gefitinib, erlotinib, or afatinib as the 1L treatment between 2012 and 2018 were included. Survival outcomes, subsequent therapies, and treatment patterns were analyzed.
Results
Among the 9,478 patients included, gefitinib (56.68%) was the most commonly prescribed 1L EGFR-TKI, followed by afatinib (25.30%) and erlotinib (18.02%). The median time to next treatment was 16.4 to 18.8 months. Overall survival (OS) was significantly different among the three treatment groups; the median OS was 28.8, 25.3, and 23.9 months for patients who were treated with afatinib, gefitinib, and erlotinib, respectively (p < 0.001). For the patients who received second-line (2L) therapy (n = 4,904, 51.74%), pemetrexed monotherapy was most commonly used (47.70%), followed by osimertinib (21.59%). Patients who received osimertinib as the 2L treatment had longer OS compared to those receiving pemetrexed (median OS: not reached vs. 25.3 to 28.8 months).
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer mortality world-wide and in South Korea [1,2]. However, the implementation of screening programs, smoking cessation, and advancements in treatment modalities have led to improved survival rates in patients with lung cancer [3,4]. The 5-year relative survival rate in lung cancer patients from South Korea has improved from 12.5% (1993–1995) to 30.2% (2013–2017) [5]. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases. The discovery of specific driver mutations and application of immunotherapy have served as breakthroughs in the treatment of metastatic NSCLC [5].
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) are an important class of agents for the targeted therapy of advanced NSCLC with EGFR-activating mutations [6]. The incidence of EGFR mutations is higher among the Asian population than among the people in Western countries, with the South Korean population displaying high rates, with 34.3% for NSCLC and 43.3% for adenocarcinoma [7]. EGFR mutation positivity is predictive for better overall survival (OS), and EGFR-TKIs have been found to be more effective and better tolerated than chemotherapy [8,9]. Consequently, testing for EGFR mutations is a crucial step in the treatment decision process, and EG- FR-TKIs are the recommended first-line (1L) treatment for patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced NSCLC [6].
Starting from gefitinib, several EGFR-TKIs have been approved and used in South Korea for the management of EGFR-positive NSCLC based on the positive results of clinical trials. Clinical trials are meticulously designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of treatments under controlled conditions. They have limitations in that they may not fully reflect real-world patient outcomes [10]. Currently, nationwide data on Korean patients with EGFR-positive NSCLC are lacking. The purpose of this real-world investigation was to describe the treatment outcomes and patterns in patients who received 1L EGFR-TKIs.
In South Korea, the National Health Insurance policy is availed by approximately 98% of the total population [11]. The Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service of Korea (HIRA) generates data as part of the reimbursement procedure for healthcare providers operating under the National Health Insurance system. The HIRA database contains various particulars, such as a distinct identification number for each patient, demographic characteristics, diagnoses categorized by the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes, pharmacy claims, examinations, and treatment records. Therefore, the HIRA database can be used as a source to analyze data from Korean patients who have received treatment with 1L EGFR-TKIs. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Ajou University Hospital (approval number: AJOUIRB-EXP-2018-490). The IRB waived the requirement for informed consent because the data were de-identified in this study.
Based on the data in the HIRA database, a total of 151,340 patients were diagnosed with the ICD code “C34” for lung cancer from January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2018. Of these, 52,622 patients who underwent lung surgery were excluded. Among the remaining 98,718 patients, 48,825 received chemotherapeutic agents used for NSCLC, such as docetaxel, gemcitabine, paclitaxel, pemetrexed, irinotecan, vinorelbine, carboplatin, cisplatin, EGFR-TKIs, or anaplastic lymphoma kinase TKIs after lung cancer diagnosis. Finally, 9,478 who received gefitinib, erlotinib, or afatinib as 1L treatment were selected as the target population for this study (Fig. 1). In South Korea, the use of gefitinib, erlotinib, and afatinib were approved for reimbursement by the Korean National Health Insurance Service as 1L therapies for EG- FR-mutant NSCLC in April 2011, March 2013, and October 2014, respectively.
The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the survival outcomes of patients with NSCLC who received EG- FR-TKIs as the 1L treatment. Time to next treatment (TTNT) was defined as the time from the start date of index treatment to the start date of the next line of treatment or the date of death. If a patient had not received subsequent treatment or had not died, they were censored at the last verified recorded date. OS was calculated as the time from the start date of 1L EGFR-TKIs to the date of death or the last known follow-up date. Patients were censored if they were still alive at the cut-off date of December 31, 2019. Dates of death were extracted from the insurance dataset. If the date of death and any verified records of visits to the outpatient or inpatient clinic during the six-month period preceding December 31, 2019 could not be identified, the patient was considered deceased. Kaplan–Meier method was used to estimate the median and 95% confidence interval (CI) for the time to event data. The log-rank test was used to evaluate survival differences between different treatment groups, with a threshold of p < 0.05 for statistical significance.
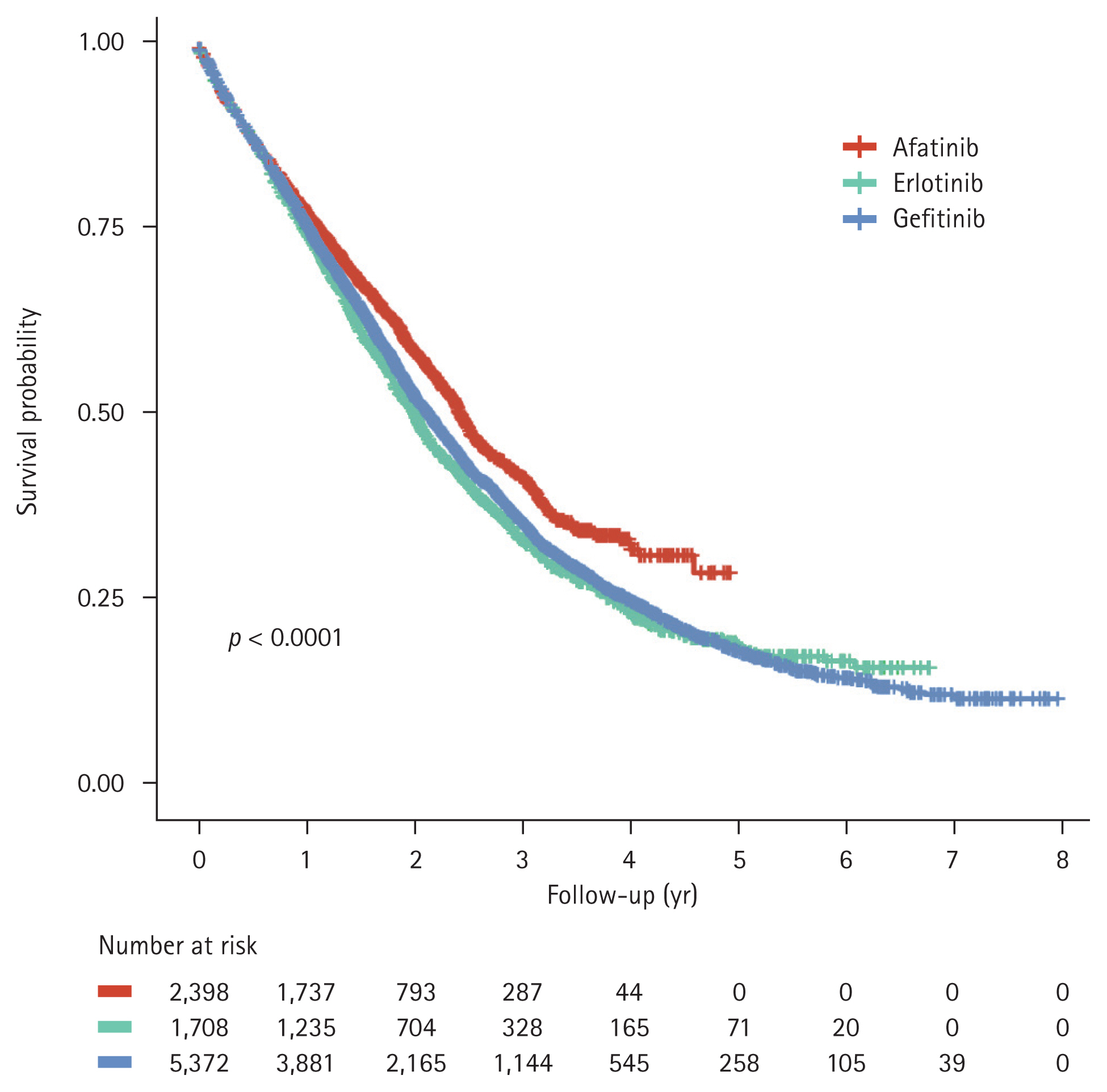
Gefitinib was the most commonly prescribed 1L EGFR-TKI, accounting for 56.68%, followed by afatinib (25.30%) and erlotinib (18.02%). The use of afatinib has gradually increased, accounting for 16.63% of all 1L EGFR-TKIs used in 2015 and 40.57% in 2018. The median TTNT was 18.8 months (95% CI, 18.0–19.8), 18.6 months (95% CI, 17.9–19.3), and 16.4 months (95% CI, 15.5–17.4) for patients who received afatinib, gefitinib, and erlotinib, respectively (p < 0.0001, Fig. 2). The 1-year TTNT rates were 71%, 69%, and 63% for the afatinib, gefitinib, and erlotinib groups, respectively. At the time of data cut-off, mortality was observed in 46.4% of patients using afatinib, 65.3% of patients using gefitinib, and 66.9% of patients using erlotinib. There was a significant difference in OS between the three groups (p < 0.0001, Fig. 3); median OS was longer for patients receiving afatinib (28.8 months; 95% CI, 27.8–30.1) than that for patients receiving gefitinib (25.3 months; 95% CI, 24.4–26.2) or erlotinib (23.9 months; 95% CI, 22.4–24.8).
Among all patients, 4,904 (51.74%) received second-line (2L) therapy, 2,578 (52.57%) received third-line, and 1,195 (46.35%) received fourth-line treatment. The subsequent treatment patterns after the failure of 1L EGFR-TKI-based therapy are shown in Table 1. For the 2L therapy, pemetrexed monotherapy was the most commonly used (n = 2,339, 47.70%), followed by osimertinib (n = 1,059, 21.59%) and platinum-based doublets (n = 855, 17.43%). As a 2L therapy, osimertinib was associated with better TTNT (the interval between 2L treatment initiation and third-line treatment initiation) than that associated with pemetrexed; the median TTNT ranged from 12.2 to 17.8 months for patients who received osimertinib and 5.3–6.4 months for those who were treated with pemetrexed (Fig. 4). The TTNT for those who received 2L osimertinib differed significantly between the three EGFR-TKI groups (p = 0.0012, Fig. 4A); the use of osimertinib after afatinib resulted in a shorter median TTNT than that after gefitinib or erlotinib. Patients treated with 2L osimertinib had a longer OS from the start of first-line EGFR-TKI treatment than patients who received second-line pemetrexed; the median OS for patients who received osimertinib was not reached, while for those who received pemetrexed, it ranged between 25.3–28.8 months (Fig. 5).
The effect of the order in which osimertinib and pemetrexed were administered on OS were analyzed. There was no significant difference in OS between patients who received pemetrexed followed by osimertinib and those who received osimertinib followed by pemetrexed (median OS, 52.7 months vs. 58.8 months; p = 0.4170, Fig. 6).
In this retrospective cohort study using real-world Korean insurance claims data, we evaluated survival outcomes in 9,478 patients with NSCLC who received 1L first-(1G) or second-generation (2G) EGFR-TKIs. Our study showed that patients with tumors harboring EGFR mutations had a median OS ranging from 23.9 to 28.8 months when treated with the three EGFR-TKIs, which was comparable to the results reported in their randomized clinical trials [12–16]. Similarly, a recent real-world study in the USA (n = 1,029) reported a median OS of 27.2 months (95% CI, 25.9–30.0) in patients in whom 1G or 2G EGFR-TKIs were administered between 2011 and 2018 [17]. In our study, the OS of patients treated with afatinib was longer than that of patients treated with 1G EGFR-TKIs. The LUX-LUNG 7 study, which compared afatinib with gefitinib as 1L treatment, demonstrated that afatinib significantly improved response rate and progression-free survival (PFS), although it was associated with more serious drug-related adverse events and frequent dose reductions [16]. While the improvement in OS with afatinib did not reach statistical significance, younger patients (< 65 years) showed an OS benefit [18]. Based on these findings, the better OS in the afatinib group may be explained by the preferential use of afatinib in fitter patients, such as those who are younger and have a better performance status, in the real-world clinical setting [19].
TTNT and time to treatment discontinuation (TTD) are endpoints used to assess treatment efficacy in real-world oncology data and can serve as proxies for PFS [20]. TTD, also called time on treatment, is defined as the duration from the initiation of the index treatment to the date of treatment discontinuation, regardless of the reason for discontinuation, including toxicity, disease progression, or death [21]. We used TTNT as the endpoint because the HIRA database does not provide information on drug discontinuation and disease progression dates. The median TTNT of 16.4 to 18.8 months in our study was longer than the median PFS of 10–14 months observed in clinical trials using 1G or 2G EGFR-TKIs [6]. Our findings should be interpreted cautiously because TTNT may be longer than real-world PFS [20]. Another explanation for this difference could be that, in clinical practice, EGFR-TKIs are occasionally continued after disease progression, particularly in cases of oligoprogression in which local therapy is employed [22].
Detection of the acquired EGFR T790M mutation is crucial, as it guides subsequent treatment strategies and predicts prognosis [1]. Current therapeutic options in T790M-negative tumors are predominantly limited to cytotoxic chemotherapy with low-response rates. While the T790M mutation is detected, third-generation EGFR-TKIs are the standard of choice for 2L or subsequent treatment. Our study revealed the prognostic significance of acquired T790M mutation. Patients who received osimertinib treatment experienced an increased survival time (> 4 years) compared with those who did not. A recent Korean study showed a median OS of 36.7 months (95% CI, 30.9 to not reached) from the time of initiation of osimertinib [23]. These findings indicate that the detection of the acquired T790M mutation after the failure of 1G or 2G EGFR-TKIs is crucial. Although the T790M mutation accounts for 50% of the resistance mechanisms to early generation EGFR-TKIs [24], our study showed that only approximately 20% of patients received osimertinib as a 2L treatment. This observation can be explained by the fact that 2L osimertinib was approved for insurance coverage in South Korea in December 2017 for patients with EGFR T790M mutation. However, it suggests that identifying the acquired T790M mutation in a real-world clinical setting is challenging. The relatively longer OS observed in patients treated with osimertinib in our study, compared to that of the 1L osimertinib group in the FLAURA study [25], suggests that sequential treatment with early generation EGFR-TKIs followed by osimertinib may be an effective strategy to maximize survival benefits. Identifying patients at diagnosis who are likely to acquire the T790M mutation after early generation TKI treatment could be crucial for selecting personalized treatment approaches. Recent studies indicate that radiomics hold promise in predicting the emergence of the acquired T790M mutation at the time of diagnosis [26,27].
In our study, the use of osimertinib after afatinib resulted in a shorter median TTNT than that observed after gefitinib or erlotinib. Conversely, other studies reported a longer PFS of osimertinib in the afatinib group than in the 1G TKI group [28,29]. Drawing a conclusion regarding the impact of different 1L EGFR-TKIs on the clinical outcome of subsequent osimertinib treatment in patients with acquired T790M mutation is challenging because several factors could affect the efficacy of 2L osimertinib. Recent studies revealed that tumor genomic complexity increased over the course of EGFR-TKI treatment and other resistance alterations co-occurred with T790M mutation during 1L therapy [28,30,31]. These accompanying alterations can affect the response of osimertinib [32]. Clinical features such as age, performance status, and hepatic metastases could be associated with outcome in patients receiving 2L osimertinib [23,33,34]. It is crucial to acknowledge the possibility of differences in these molecular and clinical features that could influence the efficacy of osimertinib between treatment groups. The limitation of our study is that we could not incorporate such detailed information into the analysis due to its unavailability in the HIRA database.
Currently, no optimal chemotherapy regimen has been established for patients with T790M-negative metastatic NSCLC whose disease has progressed on early generation EGFR-TKIs [35]. Platinum doublet chemotherapy, including pemetrexed and carboplatin, is considered one of the treatment options for eligible patients. In our study, pemetrexed monotherapy was the most commonly used regimen because the combination of pemetrexed and platinum was not covered by the insurance system until October 2019. Interestingly, a recent study comparing the effectiveness of pemetrexed plus cisplatin with pemetrexed alone in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status 0 or 1 who have failed 1L EGFR-TKIs revealed that there were no statistically significant differences in terms of PFS and OS between the two treatment arms [36].
Osimertinib has been shown to result in significantly longer PFS and OS than 1G EGFR-TKIs in patients with common EGFR mutations (exon 19 deletion or L858R mutation), making it a preferred option for 1L treatment in EGFR-mutant NSCLC [37]. A recent real-world study based on a US claims database revealed that osimertinib has become the most commonly prescribed 1L EGFR-TKI since 2018 [38]. However, this situation differs in South Korea. The 1L treatment of osimertinib was approved in December 2018, but it was not covered by the national insurance until January 2024. Consequently, we were unable to obtain real-world data on the use of osimertinib in a 1L setting. Notably, data supporting superior OS associated with 1L osimertinib therapy could not be obtained in the Asian subset analysis of the FLAURA trial [25] and the FLAURA China study [39]. Therefore, future real-world studies evaluating the use of 1L osimertinib are necessary to provide a comprehensive understanding of its impact on long-term outcomes in Korean patients.
In conclusion, our real-world study involving patients with NSCLC who were treated with 1G or 2G EGFR-TKIs revealed a comparable median OS of 23.9 to 28.8 months, consistent with the findings from randomized clinical trials. Our study also highlighted the importance of detecting the acquired T790M mutation after failure of early generation EGFR-TKIs or subsequent chemotherapy, as patients who received osimertinib treatment showed improved survival. Future real-world studies are warranted to evaluate the impact of third-generation EGFR-TKIs, including osimertinib and lazertinib, for 1L treatment and to further understand their long-term outcomes in Korean patients.
1. Real-world outcomes of 1L EGFR-TKI therapy in Korean NSCLC patients demonstrate median overall survival of approximately 2 years, highlighting the efficacy of targeted therapy in this population.
2. Detection of the acquired EGFR T790M mutation after 1G or 2G EGFR-TKI failure is crucial, as subsequent treatment with osimertinib significantly improves survival, emphasizing the importance of molecular testing in treatment decision-making.
3. Differences in treatment patterns and outcomes among EGFR-TKIs suggest the need for further investigation into optimal sequencing strategies, particularly regarding the use of third-generation EGFR-TKIs in 1L therapy, to better inform clinical practice and improve long-term outcomes for Korean NSCLC patients.
Notes
CRedit authorship contributions
Young Saing Kim: formal analysis, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing; Eun Young Lee: data curation, formal analysis, software; Hyun Woo Lee: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, resources, writing – review & editing, funding acquisition; Jin-Hyuk Choi: conceptualization, supervision; Tae-Hwan Kim: resources, writing – review & editing; Yong Won Choi: investigation, writing – review & editing; Mi Sun Ahn: investigation, writing – review & editing
Figure 1
Flow chart of the study cohort. CT, chemotherapy; OP, operation; EGFR-TKIs, epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase. a)Chemotherapy includes the following agents: afatinib, erlortinib, gefitinib, olmutinib, osimertinib, docetaxel, gemcitabine, paclitaxel, pemetrexed, irinotecan, vinorelbine, alectinib, ceritinib, crizotinib, carboplatin, and cisplatin.
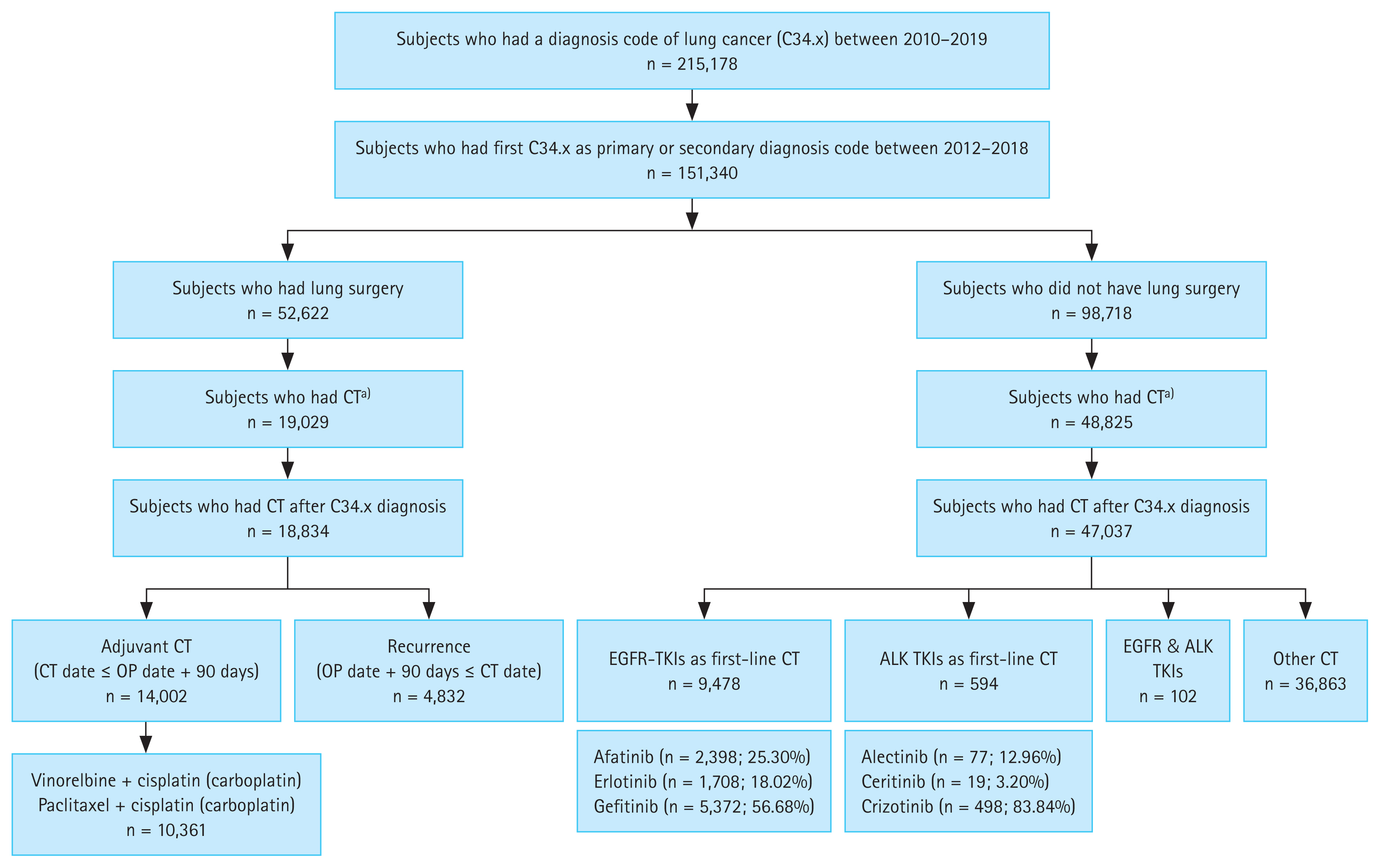
Figure 2
Kaplan–Meier curves for time to next treatment with first-line EGFR-TKIs. EGFR-TKIs, epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
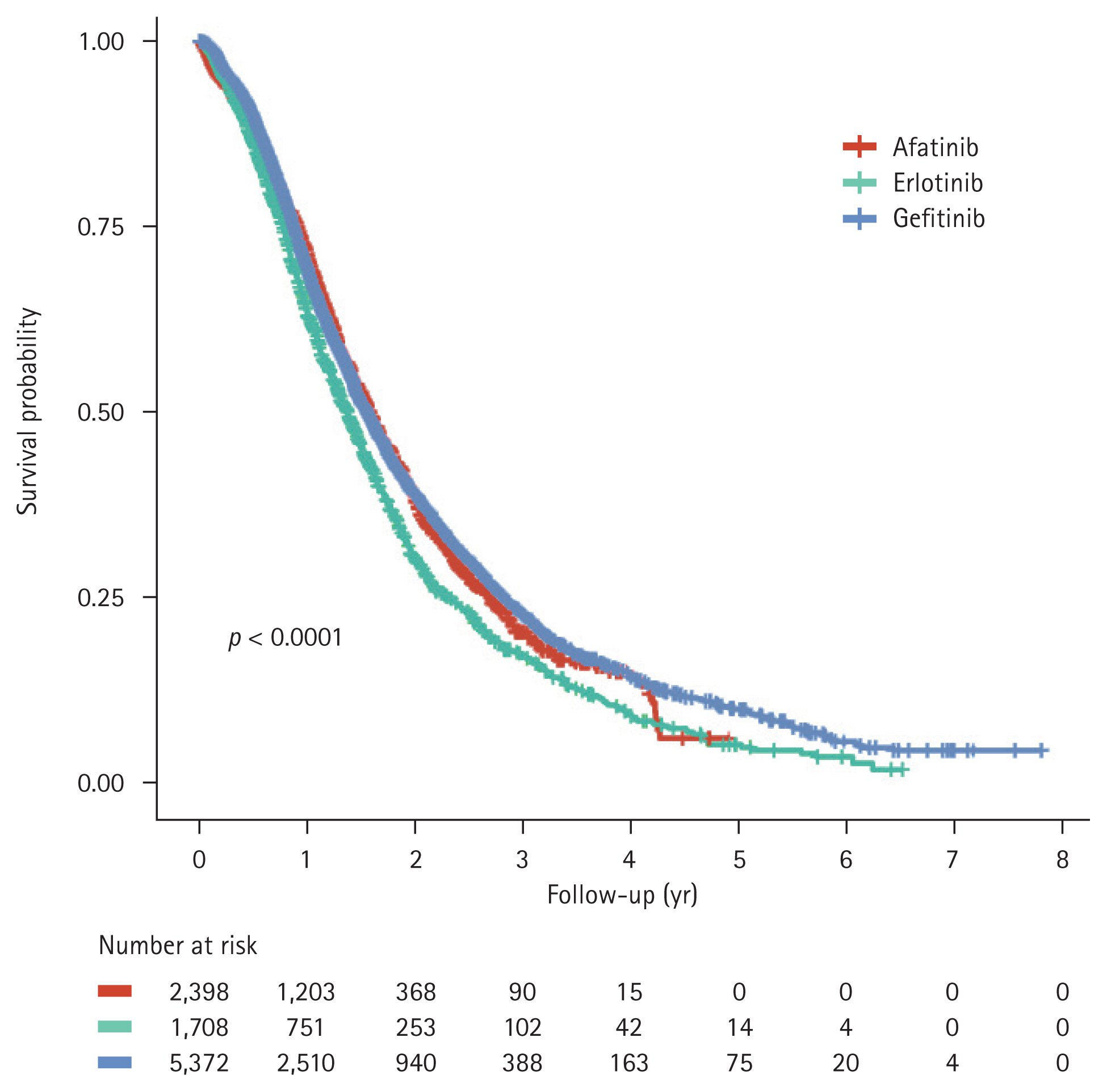
Figure 4
Time to next treatment associated with second-line osimertinib (A) and pemetrexed (B) treatments.
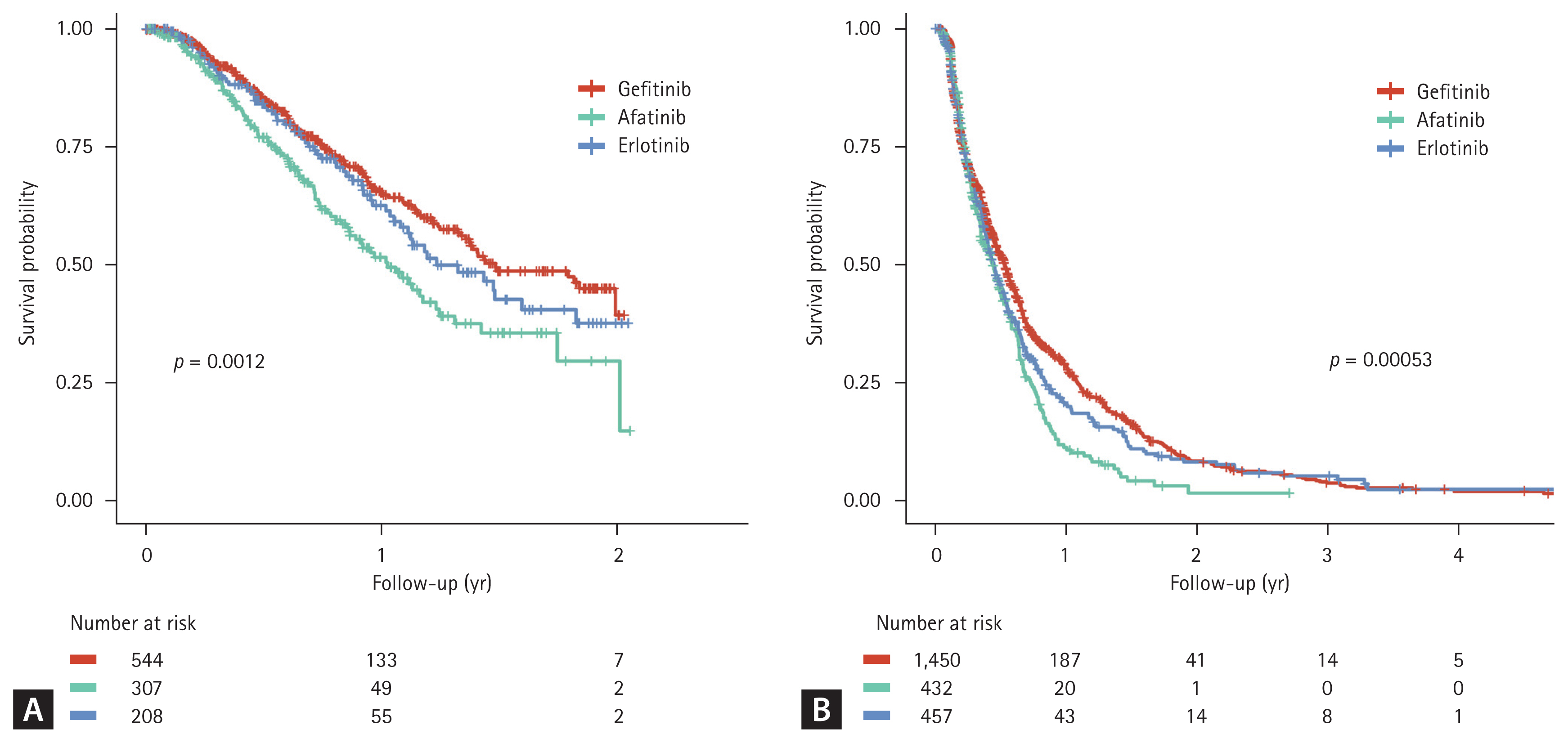
Figure 5
Kaplan–Meier curves for overall survival in patients who received second-line osimertinib or pemetrexed treatments.
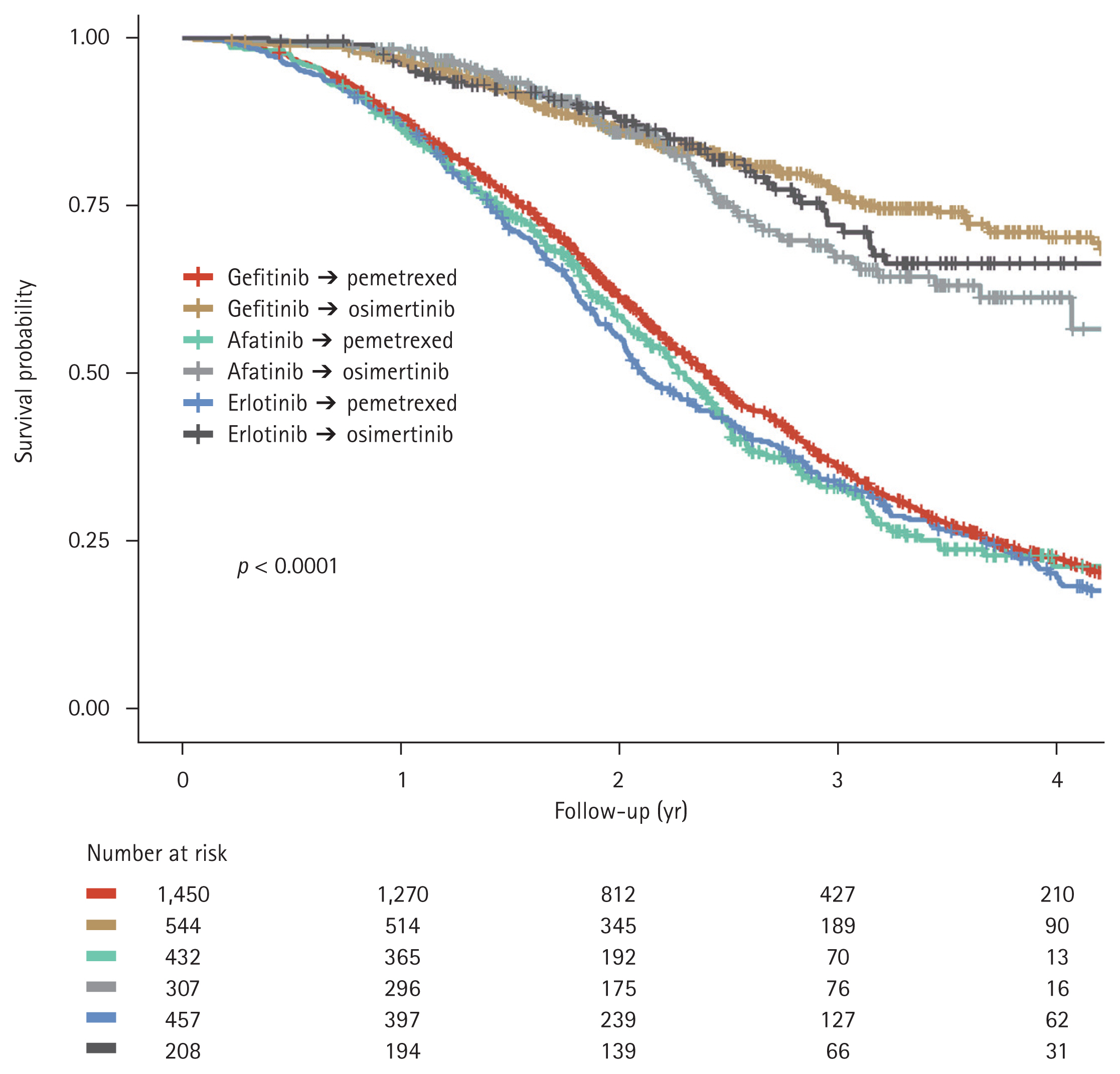
Figure 6
Kaplan–Meier curves for overall survival in patients who received different second- and third-line treatment sequences: pemetrexed followed by osimertinib, and osimertinib followed by pemetrexed. 1L EGFR-TKIs, first-line epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
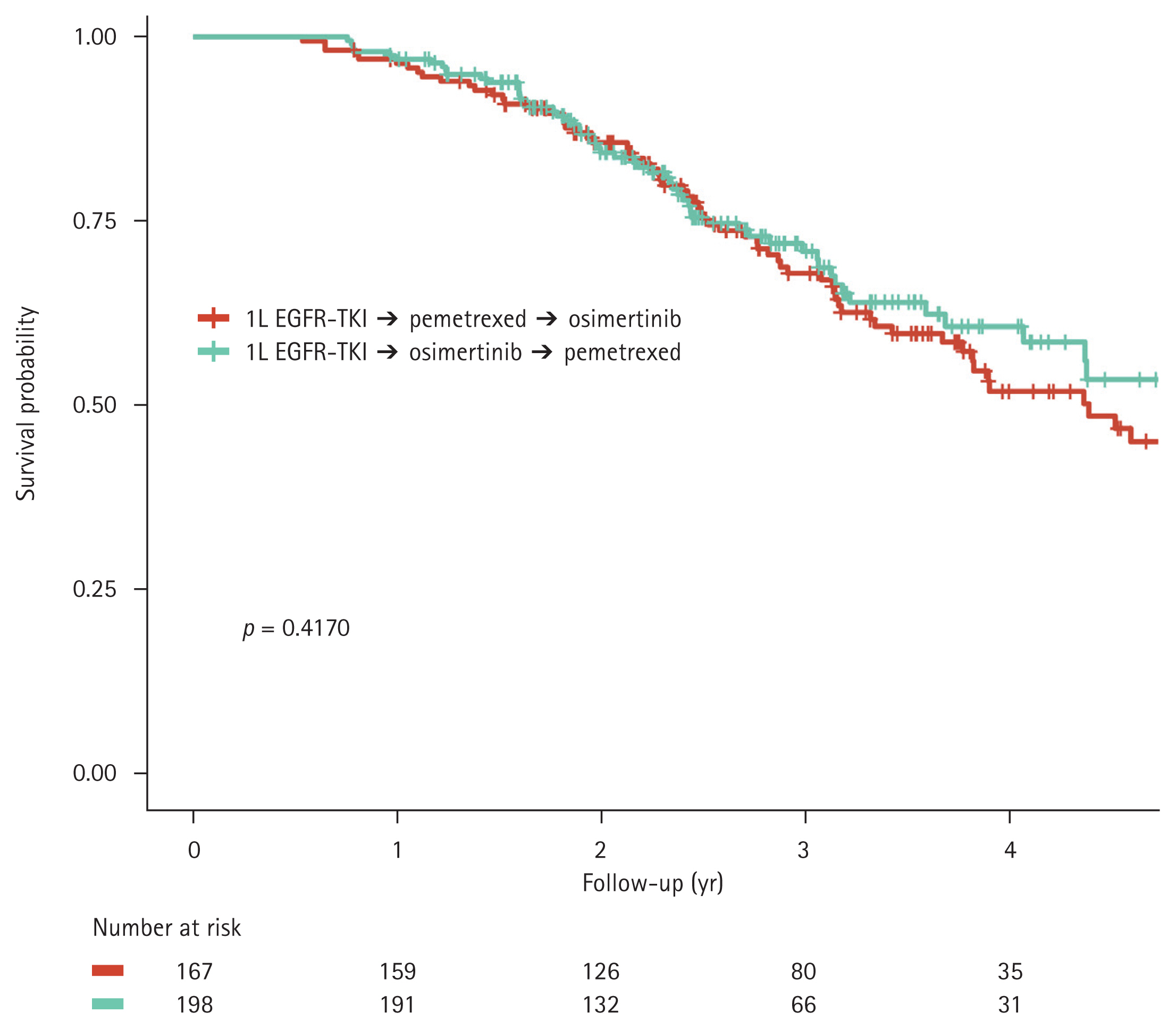
Table 1
Treatment patterns and sequences
| First-line therapy | Second-line therapy | Third-line therapy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
||||
| Regimen | n | Regimen | n | Rank | Regimen | n |
| Gefitinib | 5,372 | Pemetrexed | 1,450 | 1 | Gemcitabine + platinuma) | 270 |
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Osimertinib | 105 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Docetaxel | 92 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 4 | Gemcitabine | 80 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 5 | Gemcitabine + vinorelbine | 53 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Osimertinib | 544 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 97 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 28 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Platinum monotherapy | 5 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Gemcitabine + platinum | 283 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 107 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Osimertinib | 14 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Docetaxel | 12 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Erlotinib | 151 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 41 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Osimertinib | 40 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 4 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Paclitaxel + platinum | 56 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 16 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine + vinorelbine | 7 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Osimertinib | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Pemetrexed + platinum | 48 | 1 | Paclitaxel + platinum | 3 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Docetaxel | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Gemcitabine + vinorelbine | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Afatinib | 39 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 6 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Osimertinib | 5 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 3 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Platinum monotherapy | 38 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 10 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Erlotinib | 5 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Osimertinib | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Olmutinib | 27 | 1 | Osimertinib | 7 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Pemetrexed | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Gemcitabine | 15 | 1 | Vinorebline | 2 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Pemetrexed | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Docetaxel | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Docetaxel | 14 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 4 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Gemcitabine | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Paclitaxel | 11 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 1 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 1 | Gemcitabine | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Docetaxel + platinum | 11 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 4 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Erlotinib | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Gemcitabine + vinorelbine | 10 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 2 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Docetaxel | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Irinotecan + platinum | 8 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 2 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Erlotinib | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Vinorebline + platinum | 3 | 1 | Osimertinib | 1 | ||
|
|
||||||
| Vinorebline | 2 | |||||
|
|
||||||
| Afatinib | 2,398 | Pemetrexed | 432 | 1 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 86 |
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Osimertinib | 32 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Paclitaxel + platinum | 18 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 4 | Gemcitabine | 16 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 5 | Gemcitabine + vinorelbine | 12 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Osimertinib | 307 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 63 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 23 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Pemetrexed + platinum | 6 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Gemcitabine + platinum | 152 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 54 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Osimertinib | 8 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Paclitaxel + platinum | 5 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Gefitinib | 112 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 15 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Osimertinib | 12 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 4 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Erlotinib | 44 | 1 | Osimertinib | 10 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Pemetrexed | 8 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Gefitinib | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Pemetrexed + platinum | 41 | 1 | Erlotinib | 2 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gefitinib | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Paclitaxel + platinum | 37 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 6 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 4 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Gemcitabine + vinorelbine | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Platinum monotherapy | 28 | 1 | Osimertinib | 4 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Pemetrexed | 3 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Paclitaxel | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Olmutinib | 16 | 1 | Osimertinib | 4 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Pemetrexed | 3 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Gemcitabine | 7 | 1 | Erlotinib | 2 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Pemetrexed | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Paclitaxel | 3 | |||||
|
|
||||||
| Docetaxel + platinum | 2 | |||||
|
|
||||||
| Docetaxel | 2 | |||||
|
|
||||||
| Gemcitabine + vinorelbine | 1 | |||||
|
|
||||||
| Vinorebline + platinum | 1 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 1 | ||
|
|
||||||
| Erlotinib | 1,708 | Pemetrexed | 457 | 1 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 94 |
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine | 39 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Docetaxel | 33 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 4 | Osimertinib | 30 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 4 | Paclitaxel + platinum | 30 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Osimertinib | 208 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 38 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 17 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Pemetrexed + platinum | 4 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Gemcitabine + platinum | 136 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 57 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Osimertinib | 9 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Docetaxel | 7 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Gefitinib | 74 | 1 | Osimertinib | 19 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Pemetrexed | 11 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 3 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Pemetrexed + platinum | 37 | 1 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 2 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Docetaxel | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine + vinorelbine | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Paclitaxel + platinum | 29 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 7 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Osimertinib | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Afatinib | 14 | 1 | Osimertinib | 4 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Pemetrexed | 3 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Olmutinib | 13 | 1 | Osimertinib | 6 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Gemcitabine + platinum | 2 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 3 | Pemetrexed | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Gemcitabine | 10 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 1 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 1 | Irinotecan | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| 1 | Erlotinib | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Platinum monotherapy | 8 | 1 | Osimertinib | 1 | ||
|
|
||||||
| Docetaxel | 7 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 1 | ||
|
|
||||||
| Irinotecan + platinum | 6 | 1 | Paclitaxel + platinum | 2 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Pemetrexed | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Docetaxel + platinum | 4 | 1 | Pemetrexed | 2 | ||
|
|
||||||
| 2 | Irinotecan + platinum | 1 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Paclitaxel | 3 | |||||
|
|
||||||
| Gemcitabine + vinorelbine | 2 | |||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Vinorebline + platinum | 1 | |||||
REFERENCES
1. Ouyang W, Yu J, Huang Z, et al. Risk factors of acquired T790M mutation in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer 2020;11:2060–2067.



2. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:209–249.



3. Howlader N, Forjaz G, Mooradian MJ, et al. The effect of advances in lung-cancer treatment on population mortality. N Engl J Med 2020;383:640–649.



4. Steliga MA, Yang P. Integration of smoking cessation and lung cancer screening. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2019;8(Suppl 1):S88–S94.



5. Hong S, Won YJ, Park YR, Jung KW, Kong HJ, Lee ES, Community of Population-Based Regional Cancer Registries. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2017. Cancer Res Treat 2020;52:335–350.




6. Tan AC, Tan DSW. Targeted therapies for lung cancer patients with oncogenic driver molecular alterations. J Clin Oncol 2022;40:611–625.


7. Lee SH, Kim WS, Choi YD, et al.; Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group of Korean Society of Pathologists. Analysis of mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor gene in Korean patients with non-small cell lung cancer: summary of a nationwide survey. J Pathol Transl Med 2015;49:481–488.




8. Johnson ML, Sima CS, Chaft J, et al. Association of KRAS and EGFR mutations with survival in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer 2013;119:356–362.



9. Lee CK, Davies L, Wu YL, et al. Gefitinib or erlotinib vs chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung cancer: individual patient data meta-analysis of overall survival. J Natl Cancer Inst 2017;109.

10. Saesen R, Van Hemelrijck M, Bogaerts J, et al. Defining the role of real-world data in cancer clinical research: the position of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. Eur J Cancer 2023;186:52–61.


11. Kim JA, Yoon S, Kim LY, Kim DS. Towards actualizing the value potential of Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) data as a resource for health research: strengths, limitations, applications, and strategies for optimal use of HIRA data. J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:718–728.




12. Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS). J Clin Oncol 2011;29:2866–2874.


13. Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al.; Spanish Lung Cancer Group in collaboration with Groupe Français de Pneumo-Cancérologie and Associazione Italiana Oncologia Toracica. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:239–246.

14. Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Maemondo M, et al.; North-East Japan Study Group. Updated overall survival results from a randomized phase III trial comparing gefitinib with carboplatin-paclitaxel for chemo-naïve non-small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR gene mutations (NEJ002). Ann Oncol 2013;24:54–59.


15. Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. Final overall survival results from a randomised, phase III study of erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802). Ann Oncol 2015;26:1877–1883.


16. Park K, Tan EH, O’Byrne K, et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): a phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:577–589.


17. Nieva J, Reckamp KL, Potter D, Taylor A, Sun P. Retrospective analysis of real-world management of EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC, after first-line EGFR-TKI treatment: US treatment patterns, attrition, and survival data. Drugs Real World Outcomes 2022;9:333–345.




18. Paz-Ares L, Tan EH, O’Byrne K, et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: overall survival data from the phase IIb LUX-Lung 7 trial. Ann Oncol 2017;28:270–277.



19. Liang SK, Keng LT, Chang CH, et al. Treatment options of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors and subsequent systemic chemotherapy agents for advanced EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients: implications from Taiwan cancer registry cohort. Front Oncol 2021;10:590356.



20. Walker B, Boyd M, Aguilar K, et al. Comparisons of real-world time-to-event end points in oncology research. JCO Clin Cancer Inform 2021;5:45–46.


21. Jung HA, Hong MH, Lee HW, et al. Totality outcome of afatinib sequential treatment in patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer in South Korea (TOAST): Korean Cancer Study Group (KCSG) LU-19–22. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2022;11:1369–1379.



22. Lim JU. Management of oligometastasis and oligoprogression in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive NSCLC in the era of third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Lung Cancer 2021;22:e786–e792.


23. Lee JH, Kim EY, Park CK, et al. Real-world study of osimertinib in Korean patients with epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res Treat 2023;55:112–122.



24. Suda K, Onozato R, Yatabe Y, Mitsudomi T. EGFR T790M mutation: a double role in lung cancer cell survival? J Thorac Oncol 2009;4:1–4.


25. Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, et al.; FLAURA Investigators. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med 2020;382:41–50.


26. Li Y, Lv X, Wang Y, Xu Z, Lv Y, Hou D. CT-based nomogram for early identification of T790M resistance in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer before first-line epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors therapy. Eur Radiol Exp 2023;7:64.




27. Lu J, Ji X, Liu X, et al. Machine learning-based radiomics strategy for prediction of acquired EGFR T790M mutation following treatment with EGFR-TKI in NSCLC. Sci Rep 2024;14:446.




28. Miyashita Y, Ko R, Shimada N, et al. Impact of the generation of EGFR-TKIs administered as prior therapy on the efficacy of osimertinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M mutation. Thorac Cancer 2021;12:329–338.

29. Tamiya M, Tamiya A, Suzuki H, et al. Which is better EGFR-TKI followed by osimertinib: afatinib or gefitinib/erlotinib? Anti-cancer Res 2019;39:3923–3929.

30. Blakely CM, Watkins TBK, Wu W, et al. Evolution and clinical impact of co-occurring genetic alterations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Nat Genet 2017;49:1693–1704.




31. Jin Y, Bao H, Le X, et al. Distinct co-acquired alterations and genomic evolution during TKI treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with or without acquired T790M mutation. Oncogene 2020;39:1846–1859.



32. Vaclova T, Grazini U, Ward L, et al. Clinical impact of subclonal EGFR T790M mutations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancers. Nat Commun 2021;12:1780.




33. Huang YH, Tseng JS, Hsu KH, et al. The impact of different first-line EGFR-TKIs on the clinical outcome of sequential osimertinib treatment in advanced NSCLC with secondary T790M. Sci Rep 2021;11:12084.




34. Jin Y, Lin C, Shi X, et al. Impact of clinical and molecular features on efficacy and outcome of patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving second-line osimertinib. BMC Cancer 2022;22:586.




35. Hanna NH, Robinson AG, Temin S, et al. Therapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer with driver alterations: ASCO and OH (CCO) joint guideline update. J Clin Oncol 2021;39:1040–1091.

36. Yoo KH, Lee SJ, Cho J, et al. A randomized, open-label, phase II study comparing pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by maintenance pemetrexed versus pemetrexed alone in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant non-small cell lung cancer after failure of first-line EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor: KCSG-LU12–13. Cancer Res Treat 2019;51:718–726.



37. Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, et al.; FLAURA investigators. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non–small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2018;378:113–125.




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print