|
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 28(6); 2013 > Article |
|
Abstract
Nephrotic syndrome associated with Tsutsugamushi disease has not been previously reported. We are describing a case of Tsutsugamuchi disease presenting with nephrotic syndrome. A 72-year-old woman presented with fever and generalized edema. Laboratory studies revealed a leukocytosis, hypoalbuminemia, and hypercholesterolemia. Her urine protein excretion was 5.4 g/day. The anti-Tsutsugamushi antibody test was strongly positive (1:2,560). A renal biopsy was performed, and pathologic findings revealed membranous glomerulonephritis. The patient's clinical symptoms improved markedly after treatment with doxycycline.
Tsutsugamushi disease is a mite-borne infectious disease caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi, a gram negative intracellular bacterium. Clinical manifestations of Tsutsugamushi disease include maculopapular skin rashes, fever, and myalgia. This is followed by disseminated systemic vasculitis affecting the lung, liver, and kidney within days or weeks [1]. Renal involvement in Tsutsugamushi disease is not uncommon. The incidence of hematuria and proteinuria is approximately 10% to 20%, and acute renal failure can be a serious complication [2-5]. Nephrotic syndrome associated with scrub typhus has not been reported. We are describing a case of Tsutusgamushi disease in a patient initially presenting with nephrotic syndrome whose clinical symptoms improved following treatment with doxycycline.
A 72-year-old female was admitted with generalized edema. Her general medical condition had been stable for 2 weeks before presenting to the district clinic with a fever and myalgia. She had no history of renal disease. She denied taking any drug except acetaminophen for fever relief. The patient had a persistent fever and subsequently developed generalized edema. On physical examination, the patient was confused, acutely ill-looking, and showed grade 3 pitting edema of both lower extremities. An ecchymotic 3-cm plaque with a 1-cm black eschar was observed over the right lower abdomen (Fig. 1). At the time of admission, she had a blood pressure of 85/55 mmHg, a respiratory rate of 30 per minute, and a body temperature of 39.4℃. Laboratory studies revealed anemia (a hemoglobin level of 10.6 g/dL and a hematocrit of 33.0%) and leukocytosis (a white blood cell count of 17,420/mm3, neutrophils 78.4%, lymphocytes 12.3%, and monocytes 7.7%). Other relevant parameters included a total protein of 6.2 g/dL, a serum albumin of 2.5 g/dL, a blood urea nitrogen of 22.2 mg/dL, a serum creatinine of 1.57 mg/dL, and a total cholesterol of 250 mg/dL. Urinalysis revealed a 4+ proteinuria without significant casts and hematuria. The 24-hour urinary protein excretion was 5.4 g with a random urine protein to creatinine ratio of 9.14.
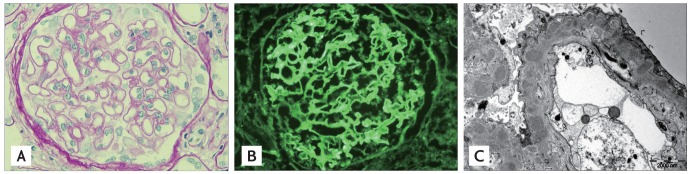
The anti-Tsutsugamushi antibody test was strongly positive (1:2,560), but was otherwise unremarkable (negative antinuclear antibody, negative anti-dsDNA antibody, negative antistreptolysin O, serum C3 82.6 mg/dL, and serum C4 20.7 mg/dL). Tsutsugamushi disease was diagnosed based on the clinical and laboratory findings. Renal ultrasound revealed normal-sized kidneys with increased echogenicity. Percutaneous renal biopsy was performed under ultrasonographic guidance to identify the cause of the nephrotic syndrome. Light microscopy of the renal biopsy specimen demonstrated diffusely and globally thickened glomerular basement membranes with subepithelial spikes and double contours (Fig. 2A). Tubulointerstitial changes were unremarkable. Immunofluorescent staining revealed fine granular deposition of immunoglobulin G along the peripheral capillary wall (Fig. 2B). Transmission electron microscopy showed that the glomerular basement membrane was diffusely thick with relatively evenly-spaced intramembranous electron dense deposits. The glomerular epithelial foot processes were diffusely effaced (Fig. 2C). Based on these pathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN).
The patient was treated with doxycycline (200 mg/day). After 5 days of treatment with antibiotics, her clinical symptoms and signs, including fever, weakness, and hypotension, greatly improved. After 4 weeks of treatment, her urinary protein:creatinine ratio was 0.9, serum albumin levels rose to 3.7 g/dL, and the edema resolved. The patient was discharged 5 weeks after admission.
Scrub typhus is a mite-borne infectious disease caused by O. tsutsugamushi. An epidemiological survey showed that the majority of Tsutsugamushi disease occurs between October and December [1]. It is difficult to differentiate Tsutsugamushi disease from other acute febrile illnesses such as leptospirosis and hemorrhagic fever due to similar clinical manifestations. This condition can be misdiagnosed as a febrile illness [2]. Tsutsugamushi disease commonly presents as an acute febrile illness 1 week to 10 days after a bite from an infected chigger mite. The major presenting symptoms are fever, severe headache, and myalgia. Other signs and symptoms include: rash, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, cough, sore throat, abdominal pain, and central nervous system involvement. The infection severity ranges from mild features to multiorgan failure and death occurring in approximately 4% of patients presenting to hospitals [1]. Acute renal failure after Tsutsugamushi disease has been reported in approximately 8% to 40% of patients, who all suffered from varying degrees of acute renal deterioration [3-5]. There are several possible mechanisms that can lead to acute renal failure after an O. tsutsugamushi infection. Vasculitis, septic shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and volume depletion may play a role in the development of acute renal failure [2].
Three cases with Tsutsugamushi disease in which a renal biopsy was performed have been reported. The pathology reports of two patients showed tubulointerstitial nephritis and one case showed minimal mesangial hyperplasia [2,3,6]. These changes could be caused by direct renal invasion from the microorganisms or a reactive response to systemic bacterial infection. Neither of these mechanisms are clearly understood at present [2]. No evidence of tubulointerstitial nephritis was found in our patient.
Yen et al. [4] reported on seven patients with Tsutsugamushi disease and acute renal failure. In that study, all patients had varying degrees of acute renal damage, but they recovered full or partial renal function following antirickettsia therapy [4].
Nephrotic syndrome has not been previously reported in patients with Tsutsugamushi disease. This paper describes the first case of nephrotic syndrome in a patient with Tsutsugamushi disease. The possibility of concurrent idiopathic MGN and Tsutsugamushi disease cannot be completely ruled out.
MGN is the most common glomerular disease resulting in nephrotic syndrome in adults. MGN can be either idiopathic or secondary. Secondary MGN is frequently associated with viral hepatitis. Many other organisms have been associated with MGN including: streptococcal infection, malaria, schistosomiasis, tuberculosis, leptospirosis, filariasis, and syphilis [7-9].
Exogenous antigens from viruses and tumors are thought to be involved in secondary forms of the disease. The nephritogenic antigen and its antibody may form an immune complex in the blood stream or in situ in the subepithelial area, which may subsequently form immune deposits. Several antigens and antibodies have been implicated in secondary MGN in humans, but the true cause remains elusive. A recent study reported that the 47-kDa protein of O. tsutsugamushi contains a trypsin domain and has significant sequence homology to human serine protease HtrA1 (hHtrA1) protein. Scrub typhus patients frequently have antibodies that react with the 47-kDa protein and also hHtrA1 [10]. We did not assay for this molecule, but this exogenous antigen may have caused the nephrotic syndrome in this case.
This report describes a patient with MGN whose proteinuria decreased dramatically after treatment with doxycycline. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of nephrotic syndrome associated with Tsutsugamushi disease.
References
1. Chang WH. Current status of tsutsugamushi disease in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 1995;10:227–238PMID : 8593201.



2. Hong JH, Oho JH, Kim JH, Kho DK. A case of acute renal failure associated with Tsutsugamushi disease. J Korean Pediatr Soc 2001;44:464–468.
3. Hsu GJ, Young T, Peng MY, Chang FY, Chou MY, Sheu LF. Acute renal failure associated with scrub typhus: report of a case. J Formos Med Assoc 1993;92:475–477PMID : 8104604.

4. Yen TH, Chang CT, Lin JL, Jiang JR, Lee KF. Scrub typhus: a frequently overlooked cause of acute renal failure. Ren Fail 2003;25:397–410PMID : 12803503.


5. Park CY, Chung CH, Kim HL, Chung JH. Tsutsugamushi infection-associated acute rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure. Korean J Intern Med 2003;18:248–250PMID : 14717236.



6. Chi WC, Huang JJ, Sung JM, Lan RR, Ko WC, Chen FF. Scrub typhus associated with multiorgan failure: a case report. Scand J Infect Dis 1997;29:634–635PMID : 9571750.


7. Barbiano Di Belgiojoso G, Genderini A, Ferrario F. Post-infectious glomerulonephritis. G Ital Nefrol 2003;20:184–199PMID : 12746805.

Figure 1
Eschar: ecchymotic 3-cm plaque with a 1-cm black eschar that was found over the right lower abdomen.
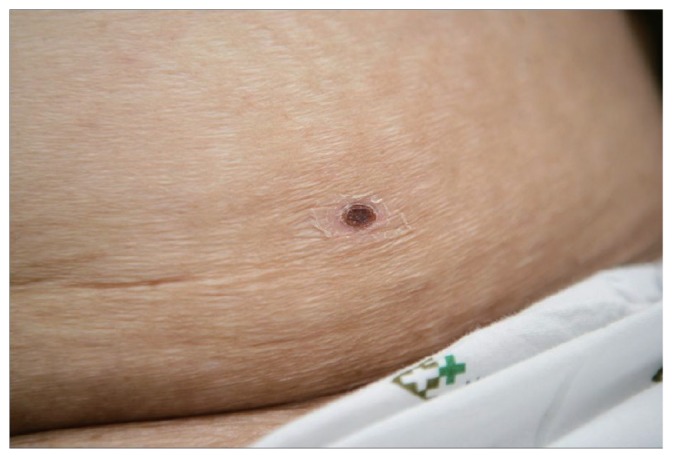
Figure 2
(A) Optical micrograph of the renal biopsy specimen showing a diffusely and globally thickened glomerular basement membrane with subepithelial spikes and double contours (periodic acid-stiff stain, × 400). (B) Immunofluorescence of fine granular deposition of immunoglobulin G along the peripheral capillary wall. (C) Electron microscopy showed that the glomerular basement membrane is diffusely thick with relatively evenly-spaced intramembranous electron dense deposits. The glomerular epithelial foot processes are diffusely effaced.
-
METRICS

- Related articles
-
A rare case of Rosai-Dorfman disease without lymphadenopathy2016 July;31(4)
Graves’ disease presenting with acute renal infarction2014 November;29(6)
A case of mediastinal ectopic thyroid presenting with a paratracheal mass2013 May;28(3)
A case of granulomatous lung disease in a patient with Good's syndrome2008 December;23(4)
A case of blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome2008 December;23(4)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print