|
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 35(3); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background/Aims
Methods
Results
Acknowledgments
Figure 1.
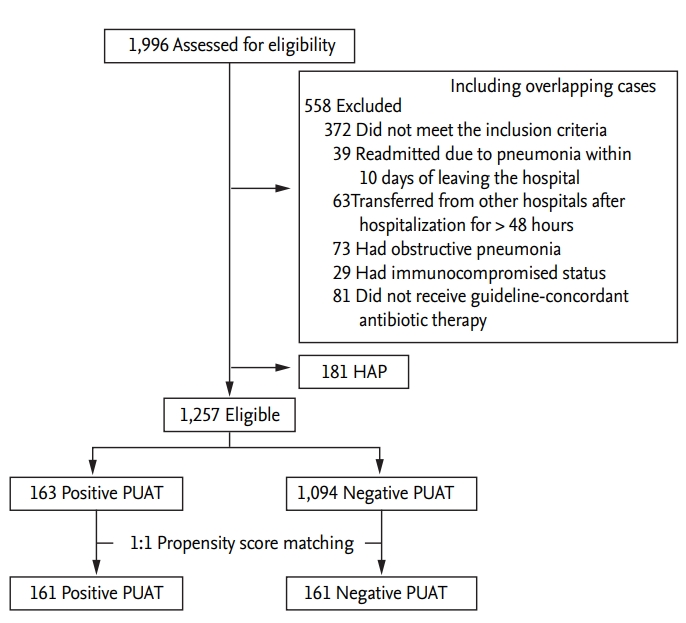
Figure 2.
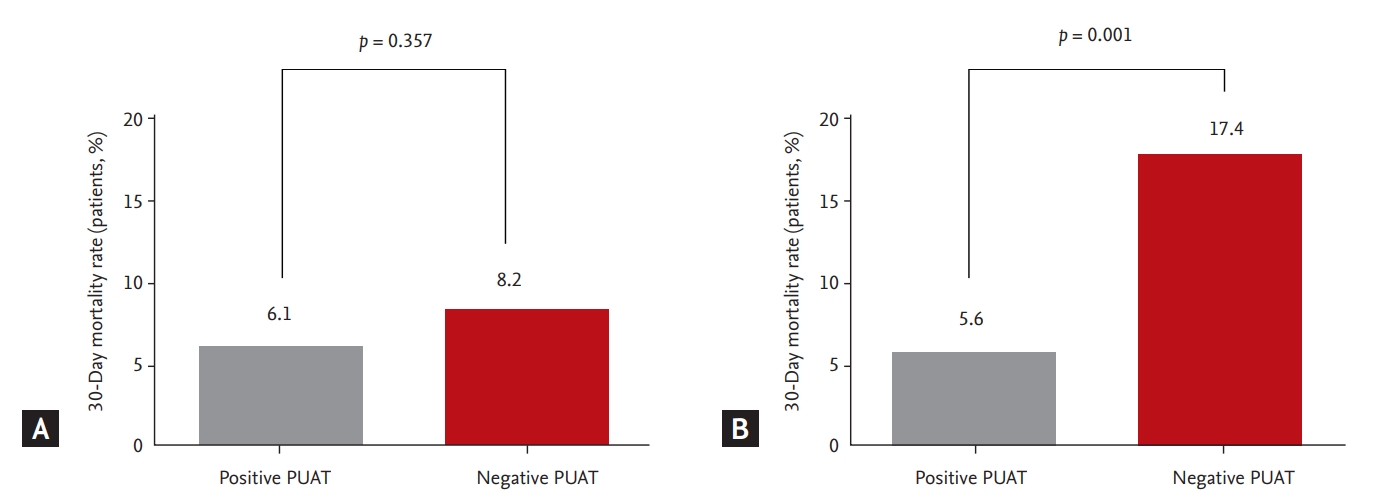
Table 1.
| Characteristic |
Entire cohort (n = 1,257) |
Propensity score-matched cohort (n = 322) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive PUAT (n = 163) | Negative PUAT (n = 1,094) | p value | Positive PUAT (n = 161) | Negative PUAT (n = 161) | p value | |
| Age, yr | 73 (66-81) | 72 (61-80) | 0.124 | 73 (66-81) | 74 (65-81) | 0.683 |
| Male sex | 105 (64.4) | 673 (61.5) | 0.477 | 103 (64.0) | 111 (68.9) | 0.345 |
| Tube feeding | 6 (3.7) | 45 (4.1) | 0.794 | 6 (3.7) | 6 (3.7) | 1.000 |
| Hospitalization for 2 or more days in the past 90 days | 25 (15.3) | 207 (18.9) | 0.271 | 25 (15.5) | 29 (18.0) | 0.551 |
| Residence in a nursing home or long-term care facility | 30 (18.4) | 139 (12.7) | 0.047 | 30 (18.6) | 29 (18.0) | 0.885 |
| Recent outpatient intravenous therapy ≤ 30 days | 6 (3.7) | 39 (3.6) | 0.941 | 6 (3.7) | 4 (2.5) | 0.551 |
| Attendance at a dialysis center in the previous 30 days | 1 (0.6) | 24 (2.2) | 0.238 | 1 (0.6) | 2 (1.2) | 1.000 |
| Comorbidity | ||||||
| Malignancya | 29 (17.8) | 197 (18.0) | 0.947 | 28 (17.4) | 27 (16.8) | 0.882 |
| Chronic liver diseaseb | 10 (6.1) | 54 (4.9) | 0.516 | 10 (6.2) | 11 (6.8) | 0.821 |
| Chronic heart diseasec | 23 (14.1) | 169 (15.4) | 0.658 | 23 (14.3) | 19 (11.8) | 0.508 |
| Chronic kidney diseased | 11 (6.7) | 126 (11.5) | 0.068 | 11 (6.8) | 16 (9.9) | 0.315 |
| Diabetes mellituse | 41 (25.2) | 251 (22.9) | 0.533 | 40 (24.8) | 48 (29.8) | 0.317 |
| Chronic respiratory diseasef | 38 (23.3) | 295 (27.0) | 0.324 | 38 (23.6) | 38 (23.6) | 1.000 |
| Central nervous system disordersg | 49 (30.1) | 264 (24.1) | 0.102 | 48 (29.8) | 54 (33.5) | 0.472 |
| Two or more comorbidities | 60 (36.8) | 436 (39.9) | 0.458 | 59 (36.6) | 66 (41.0) | 0.423 |
| Clinical parameters | ||||||
| Altered mental stateh | 15 (9.2) | 100 (9.1) | 0.980 | 15 (9.3) | 14 (8.7) | 0.846 |
| Respiratory failurei | 58 (35.6) | 359 (32.8) | 0.484 | 57 (35.4) | 62 (38.5) | 0.564 |
| Sepsis or septic shock at onsetj | 22 (13.5) | 138 (12.6) | 0.752 | 22 (13.7) | 23 (14.3) | 0.872 |
| Severe pneumonia | 26 (16.0) | 165 (15.1) | 0.773 | 26 (16.1) | 27 (16.8) | 0.881 |
| Intensive care unit admission | 21 (12.9) | 132 (12.1) | 0.745 | 20 (12.4) | 21 (13.0) | 0.867 |
| Need for ventilation | 8 (4.9) | 69 (6.3) | 0.487 | 8 (5.0) | 10 (6.2) | 0.628 |
| Radiological findings | ||||||
| Multi-lobar involvement | 86 (52.8) | 504 (46.1) | 0.127 | 84 (52.2) | 83 (51.6) | 0.921 |
| Pleural effusion | 34 (20.9) | 189 (17.3) | 0.264 | 32 (19.9) | 31 (19.3) | 0.888 |
| Laboratory findings | ||||||
| White blood cells, /mm3 | 11,600 (8,600–16,100) | 10,600 (7,675–14,100) | 0.011 | 11,600 (8,500–16,000) | 11,800 (8,650–15,850) | 0.877 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/dL | 12.0 (5.9–18.9) | 9.7 (4.2–17.2) | 0.020 | 12.0 (5.8–18.7) | 13.3 (6.3–21.7) | 0.432 |
| Indices for disease severity | ||||||
| CURB-65 score | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 0.054 | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 0.737 |
| PSI score | 98 (76–123) | 92 (70–121) | 0.080 | 98 (76–123) | 99 (76–131) | 0.610 |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%). Septic shock was defined as sepsis with persisting hypotension requiring vasopressors to maintain a mean arterial pressure of ≥ 65 mmHg and having a serum lactate level of > 2 mmol/L (18 mg/dL) despite adequate volume resuscitation.
PUAT, pneumococcal urinary antigen test; CURB-65, confusion, urea, respiratory rate, blood pressure, age ≥ 65 years; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; PSI, pneumonia severity index.
a Malignancy includes active at the time of presentation or requiring anticancer treatment within the previous 5 years.
b Chronic liver disease included preexisting viral or toxic hepatopathy at the time of pneumonia diagnosis.
c Chronic heart disease was identified based on past history or administration of diuretics for the treatment of heart disease.
d Chronic kidney disease included preexisting renal disease with documented abnormal serum creatinine levels.
e Diabetes mellitus included a history of diagnosis of intolerance to glucose, hemoglobin A1c ≥ 6.5%, or treatment with oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin.
f Chronic respiratory disease included simple chronic bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and structural lung diseases such as bronchiectasis and interstitial lung diseases.
g Central nervous system disorders included acute or chronic vascular or nonvascular encephalopathy with or without dementia.
Table 2.
Table 3.
| Variable |
Entire cohort (n = 1,257) |
Propensity score-matched cohort (n = 322) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive PUAT (n = 163) | Negative PUAT (n = 1,094) | p value | Positive PUAT (n = 161) | Negative PUAT (n = 161) | p value | |
| Microorganismsa | ||||||
| Identified pathogens | 97 (59.5) | 518 (47.3) | 0.004 | 95 (59.0) | 85 (52.8) | 0.262 |
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||||||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | 65 (39.9) | 50 (4.6) | < 0.001 | 64 (39.8) | 7 (4.3) | < 0.001 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 2 (1.2) | 43 (3.9) | 0.083 | 2 (1.2) | 9 (5.6) | 0.032 |
| Methicillin-sensitive S. aureus | 0 | 20 (1.8) | 0.096 | 0 | 6 (3.7) | 0.030 |
| Methicillin-resistant S. aureus | 2 (1.2) | 23 (2.1) | 0.762 | 2 (1.2) | 3 (1.9) | 1.000 |
| Other Gram-positive bacteria | 0 (0) | 17 (1.6) | 0.151 | 0 | 2 (1.2) | 0.498 |
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||||||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 8 (4.9) | 46 (4.2) | 0.680 | 8 (5.0) | 6 (3.7) | 0.585 |
| Haemophilus influenza | 1 (0.6) | 13 (1.2) | 1.000 | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.6) | 0.000 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 9 (5.5) | 69 (6.3) | 0.698 | 8 (5.0) | 11 (6.8) | 0.478 |
| ESBL (+) | 1 (0.6) | 8 (0.7) | 1.000 | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.6) | 1.000 |
| ESBL (–) | 8 (4.9) | 61 (5.6) | 0.727 | 7 (11.5) | 10 (6.2) | 0.455 |
| Acinetobacter species | 0 | 11 (1.0) | 0.377 | 0 | 4 (2.5) | 0.123 |
| Other Gram-negative speciesb | 2 (1.2) | 14 (1.3) | 1.000 | 2 (1.2) | 1 (0.6) | 1.000 |
| Mycoplasma pneumonia | 14 (8.6) | 61 (5.6) | 0.130 | 14 (8.7) | 9 (5.6) | 0.279 |
Table 4.
| Outcomes | Positive PUAT | Negative PUAT | p value | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary outcome | ||||
| 30-day mortality, % | ||||
| Crude (full cohort) | 6.1 | 8.2 | 0.357 | 0.73 (0.37 to 1.43)a |
| Propensity score matchingb | 5.6 | 17.4 | 0.001 | 0.28 (0.13 to 0.62)a |
| Secondary outcomes | ||||
| PDR pathogensc, % | ||||
| Crude (full cohort) | 6.7 | 9.8 | 0.216 | 0.67 (0.35 to 1.27)a |
| Propensity score matchingb | 4.3 | 10.6 | 0.034 | 0.39 (0.16 to 0.96)a |
| Duration of antibiotic therapy, day | ||||
| Crude (full cohort) | 11.1 ± 6.0 | 11.6 ± 8.2 | 0.590 | −0.50 (−1.54 to 0.54)d |
| Propensity score matchingb | 11.1 ± 6.0 | 11.9 ± 6.7 | 0.294 | −0.80 (−2.19 to 0.59)d |
| Change of antibiotics, % | ||||
| Crude (full cohort) | 17.8 | 23.0 | 0.134 | 0.72 (0.47 to 1.11)a |
| Propensity score matchingb | 17.4 | 26.7 | 0.044 | 0.58 (0.34 to 0.99)a |
| Use of inappropriate antibiotics, % | ||||
| Crude (full cohort) | 6.1 | 6.7 | 0.796 | 0.91 (0.46 to 1.81)a |
| Propensity score matchingb | 5.6 | 6.2 | 0.813 | 0.89 (0.35 to 2.26)a |
| Failure of initial antibiotic therapy, % | ||||
| Crude (full cohort) | 15.3 | 21.5 | 0.071 | 0.66 (0.42 to 1.04)a |
| Propensity score matchingb | 14.9 | 30.0 | 0.004 | 0.45 (0.26 to 0.79)a |
| Length of hospital stay, day | ||||
| Crude (full cohort) | 10.8 ± 12.0 | 9.6 ± 8.8 | 0.737 | 1.20 (−0.71 to 3.11)d |
| Propensity score matchingb | 10.9 ± 12.1 | 12.3± 10.5 | 0.153 | −1.40 (−3.87 to 1.07)d |
Values are presented as percentage or mean ± SD.
PUAT, pneumococcal urinary antigen test; PDR, potentially drug-resistant; CURB-65, confusion, urea, respiratory rate, blood pressure, age ≥ 65 years; ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase.
b The variables included as covariates in the propensity score matching were age; sex; tube feeding; comorbidities (e.g., malignancy, chronic liver disease, chronic heart disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, chronic respiratory disease, central nervous system disorders, and two or more comorbidities); altered mental state; respiratory failure; sepsis or septic shock; intensive care unit admission; need for ventilation; antibiotic use before admission; multi-lobar involvement; pleural effusion; white blood cells; C-reactive protein; CURB-65 score; and pneumonia severity index.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print