|
 |
| Korean J Intern Med > Volume 40(6); 2025 > Article |
|
See editorial "Rethinking adjunctive dobutamine in septic shock: time to individualize, not generalize" on page 861.
Abstract
Background/Aims
Despite some evidence supporting its utility, the role of adjunctive dobutamine in the management of septic shock remains unclear.
Methods
The nationwide prospective sepsis cohort of the Korean Sepsis Alliance was analyzed. Adult patients with septic shock receiving norepinephrine were enrolled over a 29-month period. Patients given a dobutamine infusion within 3 days of intensive care unit (ICU) admission were compared with patients who received no infusion. To balance baseline characteristics, propensity score matching (PSM) was used.
Results
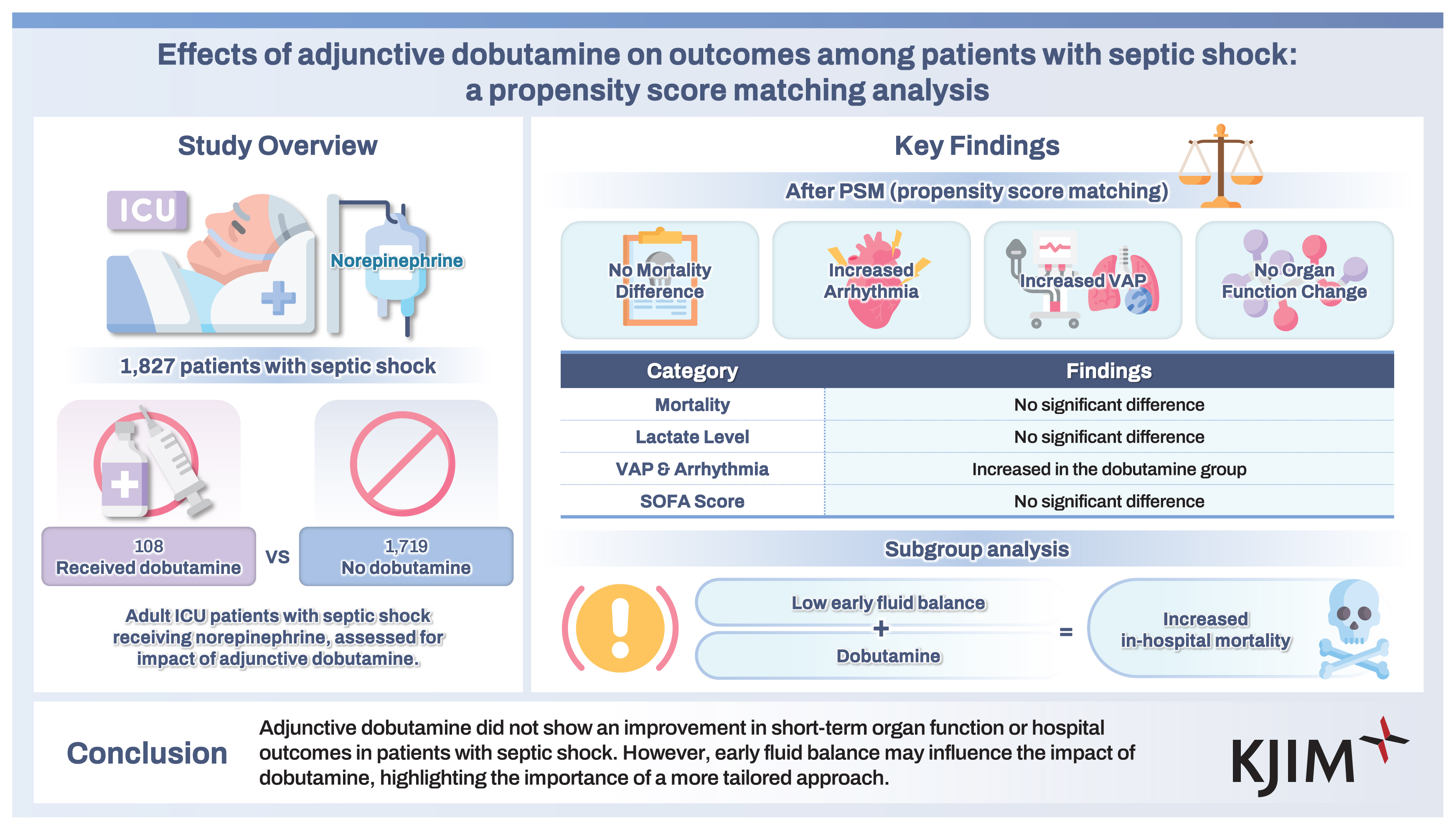
Of 11,981 patients with sepsis, 1,827 patients with septic shock receiving norepinephrine were included (108 dobutamine vs. 1,719 no dobutamine; mean age 71.4 ± 13.2 years, 59.4% male). After PSM (ratio of 1:2; 105 dobutamine patients and 209 no-dobutamine patients), Sequential Organ Failure Assessment scores and lactate levels on ICU day 3 did not significantly differ between groups. Additionally, in-hospital and ICU mortality rates did not differ between groups (54.3% vs. 48.3%, p = 0.319; 46.7% vs. 39.2%, p = 0.208, respectively). A Cox proportional model revealed that dobutamine use was not associated with in-hospital mortality (HR 1.13, 95% CI 0.81–1.58). However, subgroup analysis indicated that dobutamine use was associated with an increased risk of in-hospital mortality among patients in the lowest quintile of early fluid balance (p = 0.0286 for interaction).
Circulatory failure in septic shock arises from a combination of hypovolemia, cardiac dysfunction, and vasoplegia [1]. Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction is frequently observed in intensive care units (ICUs), with its reported prevalence in septic patients ranging from 10% to 70% depending on the definition used [2,3]. The 2021 Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines suggested adding dobutamine to norepinephrine or using epinephrine alone for patients with septic shock and cardiac dysfunction when persistent hypoperfusion remains despite adequate fluid resuscitation and arterial blood pressure [4].
While dobutamine has shown some beneficial effects on the microcirculation [5–9], clinical studies have produced mixed results regarding its efficacy [10–13], which may be partly attributable to the inotropic and vasodilatory actions of the drug, or to the inclusion of unselected patients. To date, no randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have specifically evaluated the impact of dobutamine on clinical outcomes in septic shock. Notably, one RCT reported no significant improvement in microcirculatory parameters with dobutamine administration [14], leaving it unclear whether its microcirculatory benefits translate into improved clinical outcomes [15].
Moreover, a multicenter cohort study of patients with septic cardiomyopathy found that over half of those receiving low-dose dobutamine experienced poor tolerance, associated with decreased 14-day survival [16]. An earlier study also reported paradoxical hypotension in some patients, without clear evidence of inotropic benefit [17]. These findings suggest that the effects of dobutamine may vary significantly among critically ill patients, including those with septic shock, and that its impact on mortality remains uncertain.
Nevertheless, dobutamine continues to be used as an adjunct in septic shock management and may offer potential benefits by enhancing tissue perfusion. In this study, we utilized data from a nationwide, prospective sepsis cohort to assess the effectiveness of adding dobutamine to standard vasopressor therapy, predominantly norepinephrine, in septic shock patients. Propensity score matching (PSM) was applied to mitigate potential biases and balance baseline characteristics between treatment groups.
Sepsis data from the ongoing nationwide multicenter cohort of the Korean Sepsis Alliance (KSA) were used [18,19]. Twenty university-affiliated or tertiary hospitals (21 ICUs) in South Korea with educational programs on sepsis bundles participated in this study (Supplementary Table 1); regular audits to verify data quality were conducted by KSA research committee members. We retrospectively analyzed data collected over a 29-month period (August 2019 to December 2021). All consecutive adult patients (aged ≥ 19 years) diagnosed with sepsis in emergency departments or on general wards were screened for eligibility. Sepsis and septic shock were defined in accordance with the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) [20]. The target mean arterial pressure for the use of vasopressors was ≥ 65 mmHg in patients with septic shock.
This study enrolled patients with septic shock who received norepinephrine (and vasopressin when needed) at ICU admission. Patients who received inotropes other than dobutamine (i.e., milrinone, epinephrine, or digoxin) were excluded from the study. Patients who were not admitted to an ICU or had delayed ICU admission (> 24 hours after “time zero”), do-not-resuscitate orders, or missing values were also excluded.
Study coordinators at each participating center prospectively collected data and entered them into a web-based database system (https://sepsis.crf.kr/). We obtained the following data: demographics (including age and sex); underlying comorbidities (including clinical frailty scale [CFS] score); disease severity (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment [SOFA] score and Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 [SAPS3]); physiologic and laboratory measurements; infection source and type (i.e., community- or hospital-acquired infections); the presence of multidrug resistant pathogens in the case of culture-positive patients; left ventricular systolic dysfunction (i.e., ejection fraction < 50%) by echocardiography (during ICU day 1); completion of the 3-hour Surviving Sepsis Campaign bundle; appropriateness of empirical antibiotic therapy; other treatments (during ICU day 1), such as steroids, mechanical ventilation (MV), and continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT); ICU-acquired complications (ventilation-associated pneumonia [VAP], urinary tract infection, central line-associated bloodstream infection, arrhythmia, bleeding, or cardiopulmonary resuscitation); and hospital outcomes, such as in-hospital and ICU mortality rates.
Community-onset sepsis was defined as infection occurring in a community setting, and “time zero” was defined as the time of triage in the emergency department. Hospital-onset sepsis was defined as an infection occurring within 48 hours after hospitalization, and its time zero was when the rapid response team recognized sepsis in the general ward. The appropriateness of antibiotics was determined according to the drug susceptibility test results or the relevant guidelines. Multidrug resistant pathogens were defined as microorganisms resistant to agents from at least three antimicrobial categories.
Among the enrolled patients, those who received dobutamine infusion within 3 days of ICU admission were compared with those who did not receive the infusion. The primary study outcome was in-hospital mortality. Secondary outcomes included changes in organ dysfunction as measured by SOFA scores and lactate levels by ICU day 3, ICU mortality rates, and the length of hospital stay.
PSM was used to balance the patients’ baseline characteristics. Propensity scores (i.e., the probability of receiving dobutamine) were estimated using multivariable logistic regression analysis adjusted for all pre-specified covariates, such as baseline characteristics, disease severity, and sepsis treatments (Supplementary Table 2). Dobutamine recipients were matched to non-recipients in a 1:2 ratio using nearest-neighbor matching (caliper < 0.2). Covariate balance was assessed using standard mean differences (SMDs), with an SMD ≥ 0.10 indicating imbalance.
For analytical procedures, continuous data were expressed as means ± standard deviations or medians (interquartile ranges); categorical data were expressed as frequencies (percentages). Categorical variables were compared using the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test, and continuous variables were compared using independent or paired t-tests, as appropriate. For the matched cohort, Cox proportional multivariate analysis was conducted using covariates with p values < 0.10 in univariate analyses; age and sex were included as variables because of their clinical importance, and cumulative survival rates were compared by the Kaplan–Meier method (log-rank test). Subgroup analyses were conducted to determine which patient populations showed an association between dobutamine and in-hospital mortality, focusing on the interaction between dobutamine and early fluid balance with respect to in-hospital mortality.
To examine the relationships of early fluid balance (pre-ICU admission and ICU day 1) with in-hospital mortality and dobutamine infusion, we used a restricted cubic spline regression model. We adjusted for key covariates, used three knots to optimize the model’s flexibility, and conducted separate analyses for patients with and without dobutamine treatment. The model’s effectiveness was evaluated by calculating hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and nonlinearity was assessed using the Wald test. All tests were two-sided, and p values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using R ver. 4.3.2 or IBM SPSS for Windows (ver. 25.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
This study was conducted in accordance with the amended Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) of all participating hospitals (IRB approval number: 2018-09-004 for Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital and B-1810-500-402 for Seoul National University Bundang Hospital). Because this was an observational study without interventions, any need for informed consent was determined by the ethics committees of the participating hospitals. This report follows the STROBE guidelines for observational cohort studies.
Of the 11,981 patients with sepsis registered in the KSA cohort, 4,601 were admitted to ICUs within 24 hours after time zero. We excluded patients without septic shock (n = 2,044), with missing values (n = 24), and those who received other inotropes (n = 706). Ultimately, 1,827 patients with septic shock who received norepinephrine were included (108 dobutamine and 1,719 no-dobutamine patients) in this study (Fig. 1). The mean age of the 1,827 enrolled patients was 71.4 ± 13.2 years, and 59.4% were male (Table 1). In terms of sepsis origin, the most common site was the lungs (39.1%), followed by the abdomen (31.9%) and urinary tract (17.6%). The rate of adequate empirical antibiotics was 86.7%, and pathogens were identified in 69.8% of the enrolled patients. The compliance rate with the 3-hour total sepsis bundle was 66.2% in our cohort. Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics of the enrolled patients before and after PSM.
In the entire cohort (before PSM), compared with patients in the no-dobutamine group, patients in the dobutamine group had higher lactate levels and SAPS3 and SOFA scores at ICU admission, along with higher rates of vasopressin, steroid, MV, and CRRT use (Supplementary Table 2 and 3).
After PSM, 314 patients with septic shock were identified: 105 in the dobutamine group and 209 in the no-dobutamine group (Supplementary Table 2 and 3). Supplementary Figure 1 shows a histogram of the distribution of propensity scores in the two matched groups; the SMDs of all included covariates were < 0.10, except for lactate levels (SMD = 0.1012), indicating good balance between the matched groups (Table 1 and 2, and Supplementary Fig. 1). Univariate analyses also showed no significant differences between the matched groups after PSM (all p > 0.05). Of the 314 patients, 110 underwent echocardiography within 1 day of ICU admission.
On ICU day 3, the SOFA scores and lactate levels of the matched groups did not differ, nor did their delta values (i.e., changes between ICU days 1 and 3) (Table 2). All six components of the SOFA score on ICU day 3 were also similar in the matched groups (Supplementary Table 4).
For the unmatched (entire) cohort, the in-hospital and ICU mortality rates were higher in the dobutamine group than in the no-dobutamine group (55.6% vs. 34.5%, p < 0.001; 48.1% vs. 24.3%, p < 0.001; respectively). However, after PSM, the in-hospital and ICU mortality rates and the length of hospital stay did not significantly differ between the matched groups (Table 2). The multivariable Cox model showed that dobutamine infusion was not a risk factor for in-hospital mortality in the matched cohorts; however, age, CFS, vasopressin, SOFA score, lactate level, chronic kidney disease, hematologic malignancy, and positive fluid balance were identified as significant risk factors (Table 3 and Supplementary Table 5). The Kaplan–Meier curves also showed no significant differences in cumulative survival rates between the matched groups (Fig. 2). However, regarding ICU-acquired complications, the incidences of VAP and arrhythmia were higher in the dobutamine group (Supplementary Table 6).
The subgroup analyses are shown in Figure 3 (in-hospital mortality) and Supplementary Figure 2 (ICU mortality). Among patients in the lowest quintile group for early fluid balance, the in-hospital and ICU mortality rates were higher in the dobutamine group than in the no-dobutamine group (p = 0.0286 and p = 0.0155, respectively, for interaction). Besides, among patients with a higher SAPS3 (> mean value), the ICU mortality rate was higher in the dobutamine group (p = 0.0178 for interaction); data comparing cardiovascular comorbidity and left ventricle (LV) systolic dysfunction are presented in Supplementary Table 7. In the spline regression model (Supplementary Fig. 3), no significant associations, either overall or nonlinear, were identified between early fluid balance and in-hospital mortality in either group. However, in contrast to findings in the no-dobutamine group, a lower early fluid balance tended to be associated with a higher risk of in-hospital mortality in the dobutamine group; interestingly, underlying heart disease and LV systolic dysfunction tended to be more frequent in the dobutamine group (Supplementary Table 7).
In this prospective cohort study, following confounder adjustment through PSM, we observed no enhancement in hospital outcomes or short-term organ function with adjunctive dobutamine use in septic shock patients treated with norepinephrine. Notably, patients in the dobutamine group experienced higher rates of VAP and arrhythmias. Furthermore, among those receiving dobutamine, a lower fluid balance prior to and within the first day of ICU admission was associated with increased in-hospital mortality.
Compared with previous studies, our study population was larger and PSM was used to balance baseline characteristics between the two groups. Although in-hospital and ICU mortality rates were higher in the dobutamine group than in the no-dobutamine group before PSM, we found no differences in these mortality rates between the matched groups after PSM, implying that the dobutamine group tended to have more severe illness at baseline, compared with the no-dobutamine group. This indicates the importance of similar baseline parameters between two groups in comparative observational studies [21].
Recently, Zhu et al. [13] published a study of a large number of patients in whom the use of dobutamine was associated with increased in-hospital mortality after adjustment for confounders using PSM. However, they used the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC) III database, in which the diagnosis of sepsis was based on International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 9 or 10 codes. Thus, in their study, some sepsis cases were likely undiagnosed, and it is unclear whether standardized operating procedures or treatments were performed in accordance with international sepsis guidelines. In contrast, the Korean sepsis registry we used is a nationwide prospective cohort, and participating investigators are aware of the importance of early sepsis recognition and prompt treatment: compliance with sepsis bundle components has been continuously monitored in each institution (66.2% of the study cohort), along with regular feedback. Accordingly, our data are reliable and may reflect real-world sepsis management practices. Despite the observed high in-hospital mortality rate in our study compared to previous sepsis research, we focused exclusively on a subset of patients with severe conditions (i.e., those in septic shock necessitating vasopressor support). Inclusion criteria were strictly limited to individuals for whom norepinephrine served as the initial vasopressor choice, considering vasopressin as a secondary option when necessary. Individuals receiving alternative vasopressors or inotropic agents, such as dopamine, epinephrine, digoxin, and milrinone, were intentionally excluded to minimize the potential influence of these medications and to maintain a more uniform study population.
Earlier investigations have reported the beneficial effects of dobutamine treatment. Wu et al. [12] showed that among septic shock patients with tumors, early dobutamine administration (< 3 days) was significantly associated with lower 28-day mortality, compared with patients who did not receive the drug. However, that study had a single-center retrospective design and small number of patients, leading to a high risk of bias. Although the dobutamine group in the present study also included patients who received dobutamine within 3 days after ICU admission, our findings differed from the results reported by Wu et al. [12].
Dobutamine has mixed actions on catecholamine receptors, causing increased cardiac contractibility and decreased left ventricular afterload. Although ventriculo-arterial coupling between left ventricular contractibility and left ventricular afterload should be considered, severe hypotension often occurs with dobutamine infusion [16,22]. In a study by Ergün et al. [17], 19.9% of cardiac patients had paradoxical hypotension during dobutamine infusion for myocardial scintigraphy. Recently, Razazi et al. [16] reported poor tolerance of low dose dobutamine (i.e., worsening hypotension or tachycardia) among more than half of their patients with septic cardiomyopathy. These may have been associated with heterogeneous response to the drug or greater vasodilatory effects thereof in sepsis (i.e., acidosis). However, similarly, among patients with a SAPS3 score or lactate level exceeding the mean values in the present study, subgroup analysis revealed a tendency toward higher in-hospital mortality in the dobutamine group. Taken together, these results suggest that the addition of dobutamine could be detrimental in septic shock patients with more severe illness or advanced disease. This hypothesis warrants exploration in large future RCTs.
Another notable finding was the interaction of early fluid balance and dobutamine treatment with respect to in-hospital mortality. The subgroup analysis and cubic spline regression suggested that an excessively low fluid balance had a negative impact on in-hospital mortality in the dobutamine group. Although the HR for early positive fluid balance was 1.08 (95% CI 1.00–1.16) in the multivariate analysis of all matched patients, this result may have been driven by data from the no-dobutamine group. However, considering the importance of intravascular volume in terms of increasing cardiac output and tissue perfusion, our results seem plausible and worthy of further investigation.
Thus far, no RCTs have examined the use of dobutamine in septic shock patients with cardiac dysfunction. Four previous non-RCTs of unselected populations (i.e., with or without cardiac dysfunction) showed no significant effects of dobutamine treatment on mortality or length of ICU stay [10–13]. Although several RCTs and non-RCTs revealed favorable treatment outcomes in terms of microcirculation, such as the gastric mucosa pH and PaCO2 gap (i.e., the difference between gastric mucosal and arterial PaCO2), and capillary density, these benefits were limited and the improved microcirculation has not resulted in better clinical outcomes [6,8–10,14,15,23].
In our study, we were unable to specifically assess the effects of dobutamine in patients with confirmed cardiac dysfunction due to a lack of echocardiographic data in a substantial proportion of the cases (65%), which we acknowledge as a major limitation. However, it is possible that echocardiography was performed but not formally recorded, particularly in the ICU or emergency department setting. Furthermore, dobutamine has traditionally been used as the first-line inotropic agent as part of early goal-directed therapy [24–27], and the 2016 Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines [28] have recommended its use without explicitly restricting it to patients with documented cardiac dysfunction. Therefore, some physicians in our cohort may have administered dobutamine with the intention of improving tissue perfusion, even in the absence of confirmed cardiac dysfunction. However, an RCT of dobutamine use in patients with septic cardiomyopathy (Adjunctive DobutAmine in sePtic Cardiomyopathy With Tissue Hypoperfusion), is currently underway [29], and may confirm the role of dobutamine in septic shock.
This study had some limitations. First, due to its observational nature, the results may have been affected by selection bias. To address this, we performed PSM to minimize between-group differences. Although the SMD for lactate levels remained slightly above 0.1 after matching, we further adjusted for potential confounders using a multivariable Cox regression model. Second, we could not solely focus on patients with cardiac dysfunction due to the lack of echocardiographic data for a substantial number of patients. Therefore, we cannot exclude the potential for positive effects of dobutamine in septic cardiomyopathy. Third, during the first three ICU days, the time for initiation of dobutamine infusion may have differed among enrolled patients. Although many investigators followed the international guidelines for sepsis management in this study, the exact dose and duration of dobutamine could not be determined. Additionally, analysis of interactions between vasopressor and inotrope doses—or incorporating a vasopressor-inotropic score— could have provided further information. Fourth, because this study was conducted in a single country, the generalizability of the findings may be limited. However, the data were prospectively gathered from all consecutive patients with septic shock across 20 hospitals in South Korea. Thus far, few studies have explored the effects of dobutamine treatment on patients with septic shock while accounting for confounders. Therefore, the present study may provide some insights concerning the use of dobutamine in this population.
In conclusion, adjunctive dobutamine did not enhance hospital outcomes or short-term organ recovery in septic shock patients treated with norepinephrine. Nonetheless, an early-phase low fluid balance might increase the in-hospital mortality risk for those receiving dobutamine, indicating the need for a more tailored approach to dobutamine use in septic shock.
1. In this propensity score-matched analysis, shortterm outcomes, including SOFA scores and lactate levels on ICU day 3, were not significantly affected by the adjunctive use of dobutamine.
2. The addition of dobutamine did not have a significant impact on hospital outcomes in septic shock patients receiving norepinephrine.
3. However, a low fluid balance in the early stages may be linked to an increased risk of in-hospital mortality in septic shock patients treated with dobutamine, underscoring the need for a more individualized approach to its use.
Notes
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Korean Sepsis Alliance (KSA) members: Steering Committee – Chae-Man Lim (Chair), Sang-Bum Hong, Dong Kyu oh, Su Yeon Lee, Gee Young Suh, Kyeongman Jeon, Ryoung-Eun Ko, Young-Jae Cho, Yeon Joo Lee, Sung Yoon Lim, Sunghoon Park; Participated Persons and Centers – Kangwon National University Hospital – Jeongwon Heo; Korea University Anam Hospital – Jae-myeong Lee; Daegu Catholic University Hospital – Kyung Chan Kim; Seoul National University Bundang Hospital – Yeon Joo Lee; Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital – Youjin Chang; Samsung Medical Center – Kyeongman Jeon; Seoul National University Hospital – Sang-Min Lee; Asan Medical Center – Chae-Man Lim, Suk-Kyung Hong; Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital – Woo Hyun Cho; Chonnam National University Hospital – Sang Hyun Kwak; Jeonbuk National University Hospital – Heung Bum Lee; Ulsan University Hospital – Jong-Joon Ahn; Jeju National University Hospital – Gil Myeong Seong; Chungnam National University Hospital – Song-I Lee; Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital – Sunghoon Park; Hanyang University Guri Hospital – Tai Sun Park; Severance Hospital – Su Hwan Lee; Yeungnam University Medical Center – Eun Young Choi; Chungnam National University Sejong Hospital – Jae Young Moon; Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital – Hyung Koo Kang
CRedit authorship contributions
Sung Yoon Lim: conceptualization, methodology, resources, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, writing - original draft, writing - review & editing, project administration; Kyu Jin Lee: conceptualization, methodology, resources, formal analysis, validation, writing - review & editing; Yeonhoon Jang: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, validation, software, writing - review & editing; Yeon Joo Lee: conceptualization, methodology, resources, data curation, formal analysis, validation, writing - review & editing; Ryoung-Eun Ko: methodology, resources, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, validation; Gee Young Suh: validation, software, writing - review & editing, visualization, supervision; Dong Kyu Oh: validation, software, writing - review & editing, visualization, supervision; Su Yeon Lee: validation, writing - review & editing, visualization, supervision, project administration; Mi Hyeon Park: validation, writing - review & editing, visualization, supervision, project administration; Chae-Man Lim: investigation, data curation, validation, writing - review & editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition; Sunghoon Park: conceptualization, methodology, resources, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, validation, writing - original draft, writing - review & editing, supervision
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Figure 1
Flowchart of the enrolled patients. ICU, intensive care unit, NEPI, norepinephrine; EPI, epinephrine; DOPA, dopamine; DOBU, dobutamine.
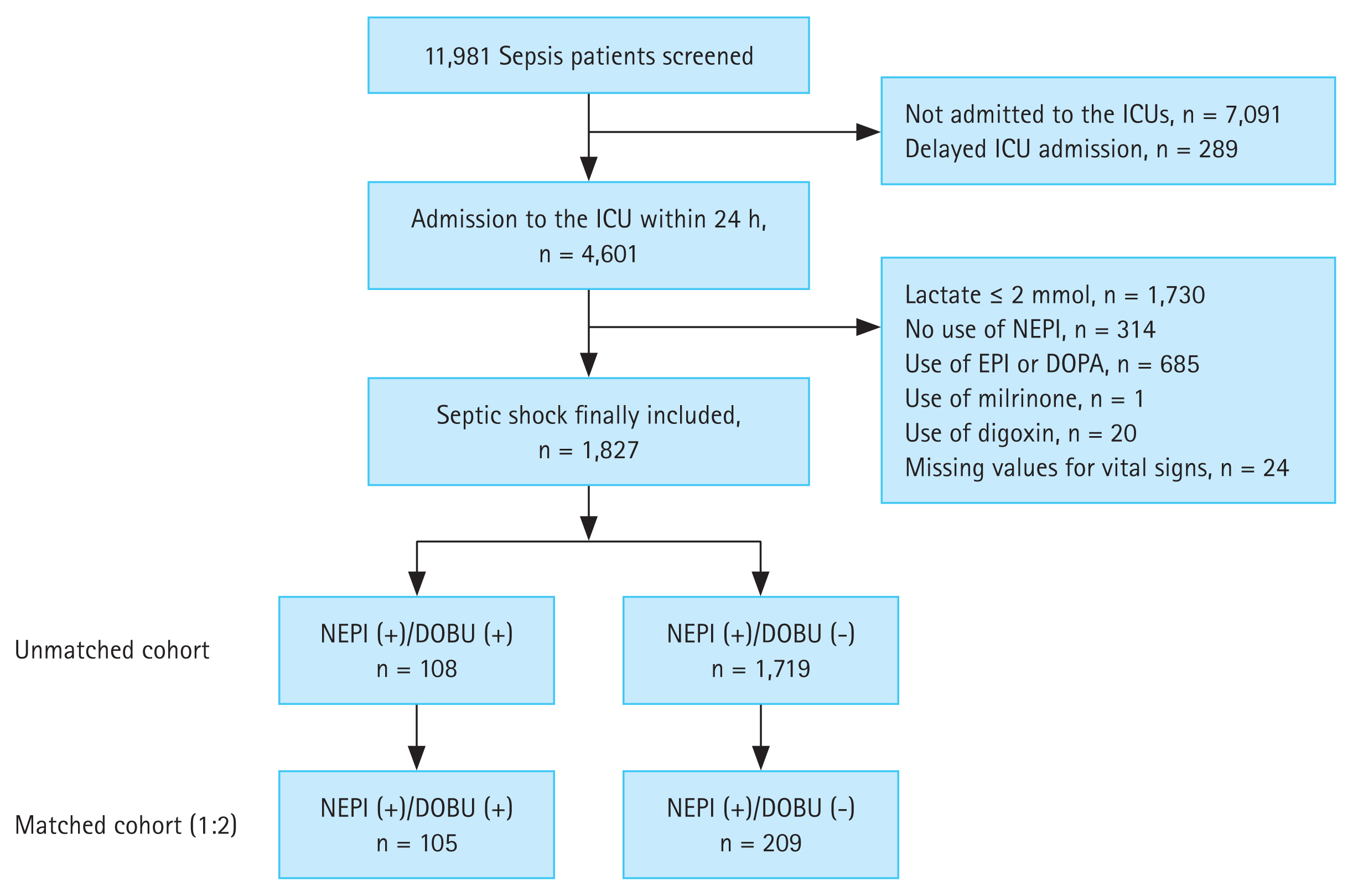
Figure 2
Kaplan–Meier curves between the matched cohorts (the dobutamine vs. non-dobutamine groups). (A) In-hospital mortality. (B) Intensive care unit mortality.
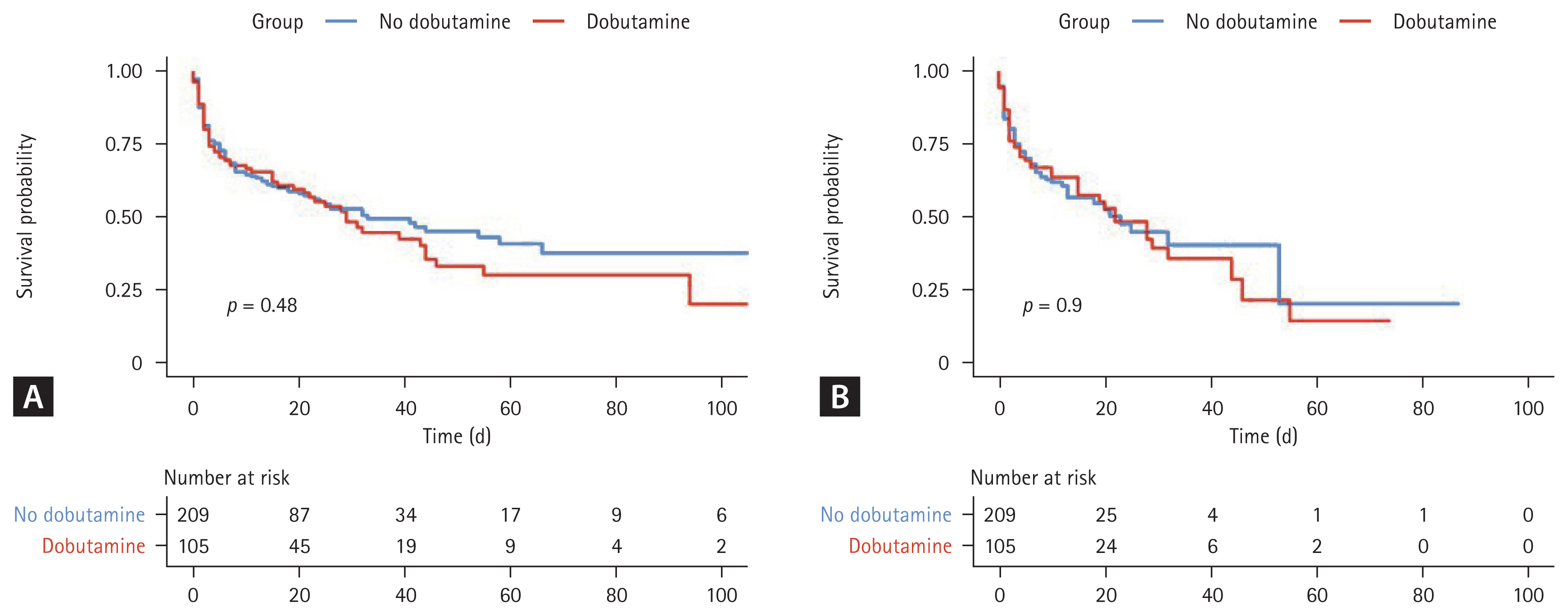
Figure 3
Forest plot for subgroup analyses among the matched cohorts for in-hospital mortality. For SAPS3, age, and lactate levels, the mean values were used to divide patients into two subgroups. MV, mechanical ventilation; SAPS3, Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3; LV, left ventricle; EF, ejection fraction; ICU, intensive care unit; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
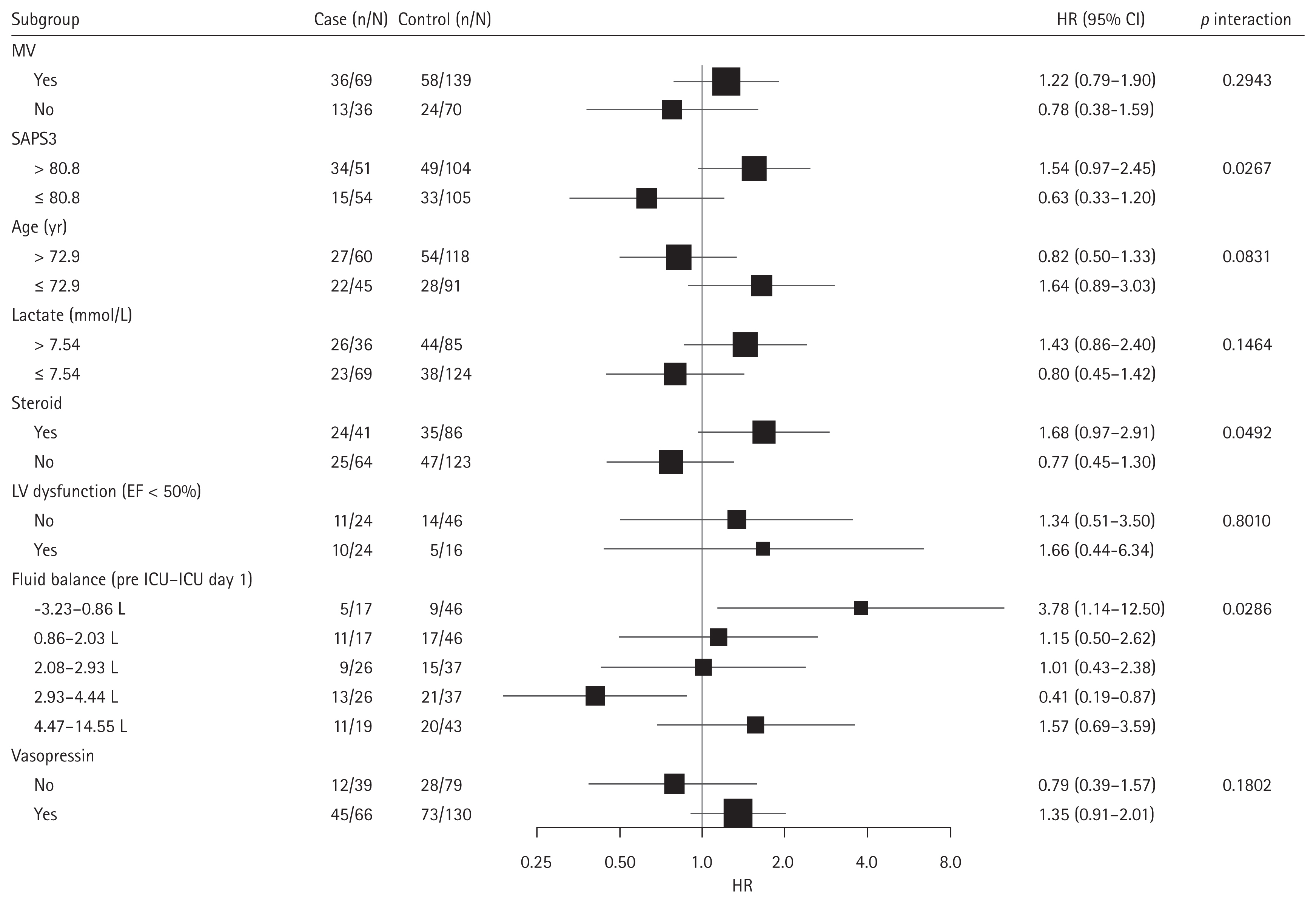
Table 1
Comparisons of baseline characteristics between dobutamine and no-dobutamine groups
| Variable | Before PSM | After PSM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| DOBU (+)(N = 108) | DOBU (−) (N = 1,719) | SMDa) | DOBU (+)(N = 105) | DOBU (−) (N = 209) | SMDa) | |
| Age (yr) | 72.9 ± 12.3 | 71.3 ± 13.2 | 0.1262 | 72.7 ± 12.4 | 73.1 ± 11.6 | −0.0344 |
|
|
||||||
| Sex, male | 58 (53.7) | 1,028 (59.8) | 0.0610 | 57 (54.3) | 121 (57.9) | 0.0381 |
|
|
||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.0 ± 3.9 | 22.2 ± 4.3 | −0.0515 | 21.9 ± 3.9 | 21.7 ± 4.3 | 0.0489 |
|
|
||||||
| CFS | 5.1 ± 2.0 | 5.1 ± 2.2 | −0.0014 | 5.1 ± 2.1 | 5.1 ± 2.2 | 0.0186 |
|
|
||||||
| SAPS3 | 81.5 ± 15.3 | 75.6 ± 14.4 | 0.3858 | 80.9 ± 14.9 | 80.8 ± 15.2 | 0.0044 |
|
|
||||||
| SOFA | 12.1 ± 3.4 | 10.6 ± 3.2 | 0.4645 | 12.1 ± 3.4 | 11.9 ± 3.4 | 0.0420 |
|
|
||||||
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 7.4 ± 5.2 | 5.5 ± 3.9 | 0.3759 | 7.3 ± 5.0 | 7.7 ± 5.1 | −0.1012 |
|
|
||||||
| Comorbidities | ||||||
|
|
||||||
| DM | 41 (38.0) | 641 (37.3) | 0.0067 | 39 (37.1) | 73 (34.9) | 0.0190 |
|
|
||||||
| Heart | 33 (30.6) | 327 (19.0) | 0.1153 | 32 (30.5) | 55 (26.3) | 0.0429 |
|
|
||||||
| Lung | 12 (11.1) | 180 (10.5) | 0.0064 | 12 (11.4) | 25 (12.0) | −0.0048 |
|
|
||||||
| Liver | 12 (11.1) | 194 (11.3) | −0.0017 | 11 (10.5) | 27 (12.9) | −0.0238 |
|
|
||||||
| CKD | 18 (16.7) | 193 (11.2) | 0.0544 | 16 (15.2) | 25 (12.0) | 0.0286 |
|
|
||||||
| CNS | 24 (22.2) | 425 (24.7) | −0.0250 | 24 (22.9) | 47 (22.5) | 0.0048 |
|
|
||||||
| Solid cancer | 21 (19.4) | 542 (31.5) | −0.1209 | 21 (20.0) | 47 (22.5) | −0.0238 |
|
|
||||||
| Hematologic cancer | 5 (4.6) | 124 (7.2) | −0.0258 | 5 (4.8) | 8 (3.8) | 0.0095 |
|
|
||||||
| Immunocompromised | 3 (2.8) | 46 (2.7) | 0.0010 | 3 (2.9) | 8 (3.8) | −0.0095 |
|
|
||||||
| CTD | 5 (4.6) | 47 (2.7) | 0.0190 | 5 (4.8) | 5 (2.4) | 0.0190 |
|
|
||||||
| COS/HOS | 62/46 | 929/790 | −0.0336 | 61/44 | 117/92 | −0.0190 |
|
|
||||||
| Site of infection | ||||||
|
|
||||||
| Abdomen | 31 (28.7) | 551 (32.1) | −0.0335 | 30 (28.6) | 60 (28.7) | 0.0000 |
|
|
||||||
| Catheter-associated | 2 (1.9) | 18 (1.0) | 0.0080 | 1 (1.0) | 4 (1.9) | −0.0095 |
|
|
||||||
| Neurology | 0 (0.0) | 8 (0.5) | −0.0047 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.0000 |
|
|
||||||
| Pulmonary | 39 (36.1) | 676 (39.3) | −0.0321 | 39 (37.1) | 88 (42.1) | −0.0524 |
|
|
||||||
| Skin & soft tissue | 4 (3.7) | 42 (2.4) | 0.0126 | 4 (3.8) | 8 (3.8) | 0.0000 |
|
|
||||||
| Unclear origin | 8 (7.4) | 126 (7.3) | 0.0008 | 8 (7.6) | 12 (5.7) | 0.0190 |
|
|
||||||
| Urinary | 24 (22.2) | 298 (17.3) | 0.0489 | 23 (21.9) | 37 (17.7) | 0.0429 |
|
|
||||||
| Pathogen identified | 83 (76.9) | 1,193 (69.4) | 0.0745 | 81 (77.1) | 153 (73.2) | 0.0381 |
|
|
||||||
| Bacteremia | 45 (41.7) | 704 (41.0) | 0.0071 | 44 (41.9) | 73 (34.9) | 0.0714 |
|
|
||||||
| Multidrug resistance | 28 (25.9) | 498 (29.0) | −0.0304 | 28 (26.7) | 45 (21.5) | 0.0524 |
PSM, propensity score matching; DOBU, dobutamine; SMD, standardized mean difference; BMI, body mass index; CFS, clinical frailty scale; SAPS3, Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; DM, diabetes mellitus; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CNS, central nervous system; CTD, connective tissue diseases; COS, community-onset sepsis; HOS, hospital-onset sepsis.
Table 2
Comparison of sepsis treatments and outcomes between dobutamine and no-dobutamine groups
| Variable | Before PSM | After PSM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| DOBU (+) (N = 108) | DOBU (−) (N = 1,719) | DOBU (+) (N = 105) | DOBU (−) (N = 209) | |||
| Sepsis treatments | SMDb) | SMDb) | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Antibiotic adequacy | 97 (89.8) | 1,503 (87.4) | −0.0238 | 95 (90.5) | 193 (92.3) | 0.0190 |
|
|
||||||
| Vasopressin | 69 (63.9) | 567 (33.0) | 0.3090 | 66 (62.9) | 130 (62.2) | 0.0048 |
|
|
||||||
| Steroid | 42 (38.9) | 386 (22.5) | 0.1643 | 41 (39.0) | 86 (41.1) | −0.0190 |
|
|
||||||
| MV | 72 (66.7) | 740 (43.0) | 0.2362 | 69 (65.7) | 139 (66.5) | −0.0095 |
|
|
||||||
| CRRT | 39 (36.1) | 304 (17.7) | 0.1843 | 36 (34.3) | 71 (34.0) | 0.0000 |
|
|
||||||
| 3-h sepsis bundle | ||||||
|
|
||||||
| Lactate measure | 105 (97.2) | 1,634 (95.1) | 0.0217 | 102 (97.1) | 201 (96.2) | 0.0095 |
|
|
||||||
| Blood culture | 68 (63.0) | 1,225 (71.3) | −0.0830 | 67 (63.8) | 134 (64.1) | 0.0000 |
|
|
||||||
| Antibiotics | 64 (59.3) | 1,161 (67.5) | −0.0828 | 62 (59.0) | 107 (51.2) | 0.0810 |
|
|
||||||
| Fluid therapy | 80 (74.1) | 1,398 (81.3) | −0.0725 | 79 (75.2) | 154 (73.7) | 0.0143 |
|
|
||||||
| Vasopressors | 67 (62.0) | 1,099 (63.9) | −0.0190 | 65 (61.9) | 134 (64.1) | −0.0238 |
|
|
||||||
| Sepsis outcomes | p value | p value | ||||
|
|
||||||
| SOFA at ICU day 3 | 11.1 ± 3.5 | 9.2 ± 4.1 | < 0.001 | 10.9 ± 3.5 | 10.7 ± 4.2 | 0.611 |
|
|
||||||
| Lactate at ICU day 3 | 4.2 ± 4.5 | 3.0 ± 3.5 | 0.016 | 4.0 ± 4.4 | 4.5 ± 5.4 | 0.424 |
|
|
||||||
| Delta SOFAa) | −0.7 ± 3.3 | −.3 ± 3.2 | 0.090 | −0.8 ± 3.4 | −1.1 ± 3.0 | 0.427 |
|
|
||||||
| Delta lactatea) | −2.0 ± 4.6 | −2.2 ± 4.0 | 0.670 | −1.9 ± 4.5 | −2.5 ± 5.9 | 0.372 |
|
|
||||||
| Death at ICU day 7 | 36 (33.3) | 371 (21.6) | 0.004 | 36 (34.3) | 76 (36.4) | 0.717 |
|
|
||||||
| ICU mortality | 52 (48.1) | 417 (24.3) | < 0.001 | 49 (46.7) | 82 (39.2) | 0.208 |
|
|
||||||
| In-hospital mortality | 60 (55.6) | 583 (33.9) | < 0.001 | 57 (54.3) | 101 (48.3) | 0.319 |
|
|
||||||
| Length of hospital stay | 15.0 (3.3, 29.8) | 15.0 (8.0, 26.0) | 0.480 | 6.0 (2.0, 17.0) | 6.0 (2.0, 11.0) | 0.443 |
Table 3
Cox multivariable model for risk factors for in-hospital mortality
REFERENCES
3. Hasegawa D, Ishisaka Y, Maeda T, et al. Prevalence and prognosis of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Intensive Care Med 2023;38:797–808.



4. Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med 2021;49:e1063–e1143.

5. Duranteau J, Sitbon P, Teboul JL, et al. Effects of epinephrine, norepinephrine, or the combination of norepinephrine and dobutamine on gastric mucosa in septic shock. Crit Care Med 1999;27:893–900.


6. Levy B, Bollaert PE, Lucchelli JP, Sadoune LO, Nace L, Larcan A. Dobutamine improves the adequacy of gastric mucosal perfusion in epinephrine-treated septic shock. Crit Care Med 1997;25:1649–1654.


7. Lisbon A. Dopexamine, dobutamine, and dopamine increase splanchnic blood flow: what is the evidence? Chest 2003;123(5 Suppl):460S–463S.


8. Wu Y, Zhang N, Wu Y, et al. Effects of dopamine, norepinephrine and dobutamine on gastric mucosal pH of septic shock patients. Exp Ther Med 2016;12:975–978.



9. Zhou SX, Qiu HB, Huang YZ, Yang Y, Zheng RQ. Effects of norepinephrine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine-dobutamine on systemic and gastric mucosal oxygenation in septic shock. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2002;23:654–658.

10. Martin C, Viviand X, Arnaud S, Vialet R, Rougnon T. Effects of norepinephrine plus dobutamine or norepinephrine alone on left ventricular performance of septic shock patients. Crit Care Med 1999;27:1708–1713.


11. Wilkman E, Kaukonen KM, Pettilä V, Kuitunen A, Varpula M. Association between inotrope treatment and 90-day mortality in patients with septic shock. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2013;57:431–442.


12. Wu YF, Pan Y, Tang Q, Lou N, Wang DF. Early administration of dobutamine in the treatment of septic shock patients with tumor-a retrospective comparative cohort study. Ann Transl Med 2022;10:828.



13. Zhu Y, Yin H, Zhang R, Ye X, Wei J. The effect of dobutamine in sepsis: a propensity score matched analysis. BMC Infect Dis 2021;21:1151.




14. Hernandez G, Bruhn A, Luengo C, et al. Effects of dobutamine on systemic, regional and microcirculatory perfusion parameters in septic shock: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover study. Intensive Care Med 2013;39:1435–1443.



15. De Backer D, Creteur J, Dubois MJ, et al. The effects of dobutamine on microcirculatory alterations in patients with septic shock are independent of its systemic effects. Crit Care Med 2006;34:403–408.


16. Razazi K, Labbé V, Laine L, et al. Hemodynamic effects and tolerance of dobutamine for myocardial dysfunction during septic shock: an observational multicenter prospective echocardiographic study. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022;9:951016.



17. Ergün EL, Caner B, Atalar E, Karanfil A, Tokgözoğlu L. Paradoxical hypotension during dobutamine infusion for myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Nuklearmedizin 1998;37:268–271.


18. Jeon K, Na SJ, Oh DK, et al.; Korean Sepsis Alliance (KSA) study group. Characteristics, management and clinical outcomes of patients with sepsis: a multicenter cohort study in Korea. Acute Crit Care 2019;34:179–191.




19. Kim JH, Kim YK, Oh DK, et al.; Korean Sepsis Alliance (KSA) investigators. Hypotension at the time of sepsis recognition is not associated with increased mortality in sepsis patients with normal lactate levels. Shock 2023;59:360–367.

20. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016;315:801–810.


21. Ross ME, Kreider AR, Huang YS, Matone M, Rubin DM, Localio AR. Propensity score methods for analyzing observational data like randomized experiments: challenges and solutions for rare outcomes and exposures. Am J Epidemiol 2015;181:989–995.


22. Boissier F, Razazi K, Seemann A, et al. Left ventricular systolic dysfunction during septic shock: the role of loading conditions. Intensive Care Med 2017;43:633–642.



23. Enrico C, Kanoore Edul VS, Vazquez AR, et al. Systemic and microcirculatory effects of dobutamine in patients with septic shock. J Crit Care 2012;27:630–638.


24. Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, et al.; Early Goal-Directed Therapy Collaborative Group. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 2001;345:1368–1377.


25. ProCESS Investigators. Yealy DM, Kellum JA, Huang DT, et al. A randomized trial of protocol-based care for early septic shock. N Engl J Med 2014;370:1683–1693.



26. Mouncey PR, Osborn TM, Power GS, et al.; ProMISe Trial Investigators. Trial of early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. N Engl J Med 2015;372:1301–1311.


27. ARISE Investigators; ANZICS Clinical Trials Group. Peake SL, Delaney A, Bailey M, et al. Goal-directed resuscitation for patients with early septic shock. N Engl J Med 2014;371:1496–1506.


28. Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med 2017;43:304–377.

29. Adjunctive DobutAmine in sePtic Cardiomyopathy With Tissue Hypoperfusion (ADAPT) [Internet] Bethesda (MD): ClinicalTrials.gov, cYEAR, [cited 2025 Oct 20]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04166331.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement figure 1
Supplement figure 1 Print
Print